Page 899 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 899
CHAPTER 49 Antiviral Agents 885
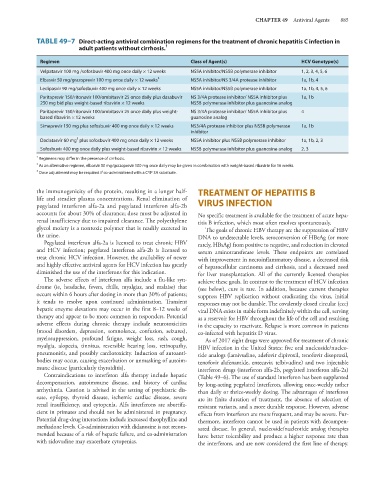
TABLE 49–7 Direct-acting antiviral combination regimens for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection in
adult patients without cirrhosis. 1
Regimen Class of Agent(s) HCV Genotype(s)
Velpatasvir 100 mg /sofosbuvir 400 mg once daily × 12 weeks NS5A inhibitor/NS5B polymerase inhibitor 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Elbasvir 50 mg/grazoprevir 100 mg once daily × 12 weeks 2 NS5A inhibitor/NS 3/4A protease inhibitor 1a, 1b, 4
Ledipasvir 90 mg/sofosbuvir 400 mg once daily × 12 weeks NS5A inhibitor/NS5B polymerase inhibitor 1a, 1b, 4, 5, 6
Paritaprevir 150/ritonavir 100/ombitasvir 25 once daily plus dasabuvir NS 3/4A protease inhibitor/ NS5A inhibitor plus 1a, 1b
250 mg bid plus weight-based ribavirin × 12 weeks NS5B polymerase inhibitor plus guanosine analog
Paritaprevir 150/ritonavir 100/ombitasvir 25 once daily plus weight- NS 3/4A protease inhibitor/ NS5A inhibitor plus 4
based ribavirin × 12 weeks guanosine analog
Simeprevir 150 mg plus sofosbuvir 400 mg once daily × 12 weeks NS3/4A protease inhibitor plus NS5B polymerase 1a, 1b
inhibitor
3
Daclatasvir 60 mg plus sofosbuvir 400 mg once daily × 12 weeks NS5A inhibitor plus NS5B polymerase inhibitor 1a, 1b, 2, 3
Sofosbuvir 400 mg once daily plus weight-based ribavirin × 12 weeks NS5B polymerase inhibitor plus guanosine analog 2, 3
1
Regimens may differ in the presence of cirrhosis.
2 As an alternative regimen, elbasvir 50 mg/grazoprevir 100 mg once daily may be given in combination with weight-based ribavirin for 16 weeks.
3
Dose adjustment may be required if co-administered with a CYP 3A substrate.
the immunogenicity of the protein, resulting in a longer half- TREATMENT OF HEPATITIS B
life and steadier plasma concentrations. Renal elimination of
pegylated interferon alfa-2a and pegylated interferon alfa-2b VIRUS INFECTION
accounts for about 30% of clearance; dose must be adjusted in No specific treatment is available for the treatment of acute hepa-
renal insufficiency due to impaired clearance. The polyethylene titis B infection, which most often resolves spontaneously.
glycol moiety is a nontoxic polymer that is readily excreted in The goals of chronic HBV therapy are the suppression of HBV
the urine. DNA to undetectable levels, seroconversion of HBeAg (or more
Pegylated interferon alfa-2a is licensed to treat chronic HBV rarely, HBsAg) from positive to negative, and reduction in elevated
and HCV infection; pegylated interferon alfa-2b is licensed to serum aminotransferase levels. These endpoints are correlated
treat chronic HCV infection. However, the availability of newer with improvement in necroinflammatory disease, a decreased risk
and highly effective antiviral agents for HCV infection has greatly of hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis, and a decreased need
diminished the use of the interferons for this indication. for liver transplantation. All of the currently licensed therapies
The adverse effects of interferon alfa include a flu-like syn- achieve these goals. In contrast to the treatment of HCV infection
drome (ie, headache, fevers, chills, myalgias, and malaise) that (see below), cure is rare. In addition, because current therapies
occurs within 6 hours after dosing in more than 30% of patients; suppress HBV replication without eradicating the virus, initial
it tends to resolve upon continued administration. Transient responses may not be durable. The covalently closed circular (ccc)
hepatic enzyme elevations may occur in the first 8–12 weeks of viral DNA exists in stable form indefinitely within the cell, serving
therapy and appear to be more common in responders. Potential as a reservoir for HBV throughout the life of the cell and resulting
adverse effects during chronic therapy include neurotoxicities in the capacity to reactivate. Relapse is more common in patients
(mood disorders, depression, somnolence, confusion, seizures), co-infected with hepatitis D virus.
myelosuppression, profound fatigue, weight loss, rash, cough, As of 2017 eight drugs were approved for treatment of chronic
myalgia, alopecia, tinnitus, reversible hearing loss, retinopathy, HBV infection in the United States: five oral nucleoside/nucleo-
pneumonitis, and possibly cardiotoxicity. Induction of autoanti- tide analogs (lamivudine, adefovir dipivoxil, tenofovir disoproxil,
bodies may occur, causing exacerbation or unmasking of autoim- tenofovir alafenamide, entecavir, telbivudine) and two injectable
mune disease (particularly thyroiditis). interferon drugs (interferon alfa-2b, pegylated interferon alfa-2a)
Contraindications to interferon alfa therapy include hepatic (Table 49–6). The use of standard interferon has been supplanted
decompensation, autoimmune disease, and history of cardiac by long-acting pegylated interferon, allowing once-weekly rather
arrhythmia. Caution is advised in the setting of psychiatric dis- than daily or thrice-weekly dosing. The advantages of interferon
ease, epilepsy, thyroid disease, ischemic cardiac disease, severe are its finite duration of treatment, the absence of selection of
renal insufficiency, and cytopenia. Alfa interferons are abortifa- resistant variants, and a more durable response. However, adverse
cient in primates and should not be administered in pregnancy. effects from interferon are more frequent, and may be severe. Fur-
Potential drug-drug interactions include increased theophylline and thermore, interferon cannot be used in patients with decompen-
methadone levels. Co-administration with didanosine is not recom- sated disease. In general, nucleoside/nucleotide analog therapies
mended because of a risk of hepatic failure, and co-administration have better tolerability and produce a higher response rate than
with zidovudine may exacerbate cytopenias. the interferons, and are now considered the first line of therapy.