Page 944 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 944
930 SECTION VIII Chemotherapeutic Drugs
I
N
H C
C CH 3
O 2 N C
N I N
CH CH OH OH
2
2
Metronidazole Iodoquinol
OH
CH OH H 2 N NH 2
2
O H N OH
2
O OH
OH COO N COCHCl 2
HO O CH NH 2 O
O O O 2 CH 3
NH 2
OH Diloxanide furoate
CH OH
2
Paromomycin
CH OH HOH C
2
2
CHOH HOHC
HN NH –
CHO OH O OHC
C OCH (CH ) CH O C
2
2 3
2
H N NH 2 CHO Sb O Sb OHC 3Na +
2
Pentamidine CHO OHC
COO – – OOC
Sodium stibogluconate
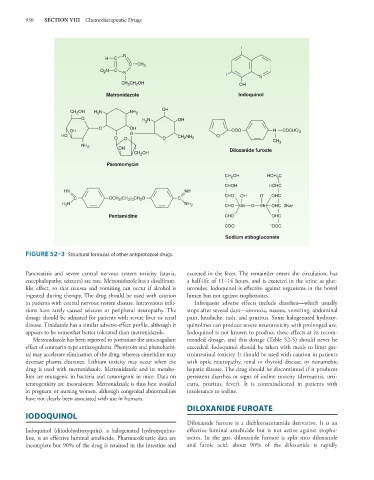
FIGURE 52–3 Structural formulas of other antiprotozoal drugs.
Pancreatitis and severe central nervous system toxicity (ataxia, excreted in the feces. The remainder enters the circulation, has
encephalopathy, seizures) are rare. Metronidazole has a disulfiram- a half-life of 11–14 hours, and is excreted in the urine as gluc-
like effect, so that nausea and vomiting can occur if alcohol is uronides. Iodoquinol is effective against organisms in the bowel
ingested during therapy. The drug should be used with caution lumen but not against trophozoites.
in patients with central nervous system disease. Intravenous infu- Infrequent adverse effects include diarrhea—which usually
sions have rarely caused seizures or peripheral neuropathy. The stops after several days—anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal
dosage should be adjusted for patients with severe liver or renal pain, headache, rash, and pruritus. Some halogenated hydroxy-
disease. Tinidazole has a similar adverse-effect profile, although it quinolines can produce severe neurotoxicity with prolonged use.
appears to be somewhat better tolerated than metronidazole. Iodoquinol is not known to produce these effects at its recom-
Metronidazole has been reported to potentiate the anticoagulant mended dosage, and this dosage (Table 52-5) should never be
effect of coumarin-type anticoagulants. Phenytoin and phenobarbi- exceeded. Iodoquinol should be taken with meals to limit gas-
tal may accelerate elimination of the drug, whereas cimetidine may trointestinal toxicity. It should be used with caution in patients
decrease plasma clearance. Lithium toxicity may occur when the with optic neuropathy, renal or thyroid disease, or nonamebic
drug is used with metronidazole. Metronidazole and its metabo- hepatic disease. The drug should be discontinued if it produces
lites are mutagenic in bacteria and tumorigenic in mice. Data on persistent diarrhea or signs of iodine toxicity (dermatitis, urti-
teratogenicity are inconsistent. Metronidazole is thus best avoided caria, pruritus, fever). It is contraindicated in patients with
in pregnant or nursing women, although congenital abnormalities intolerance to iodine.
have not clearly been associated with use in humans.
DILOXANIDE FUROATE
IODOQUINOL
Diloxanide furoate is a dichloroacetamide derivative. It is an
Iodoquinol (diiodohydroxyquin), a halogenated hydroxyquino- effective luminal amebicide but is not active against tropho-
line, is an effective luminal amebicide. Pharmacokinetic data are zoites. In the gut, diloxanide furoate is split into diloxanide
incomplete but 90% of the drug is retained in the intestine and and furoic acid; about 90% of the diloxanide is rapidly