Page 383 - House of Maxell
P. 383
DISCONTINUITY IN FEED LINES 363
7.2 DISCONTINUITIES IN PLANAR LINES
7.2.1 Introduction
We know that the majority of planar lines such as stripline, microstrip, CPW, slotline, etc.
belong to the class of open structures with the quasi-TEM mode. If so, the small sizes
discontinuities in these lines might work not only as lumped reactive elements but as electric
or magnetic dipoles, sometimes even as a Huygens’ radiator. Essentially, the equivalent circuit
of most discontinues are the same as in a coaxial line but must include some primarily resistive
components associated with the radiation loss, energy leakage, mutual coupling between
adjacent circuit elements, etc. A complete analysis of the desired accuracy may be performed
numerically only and with the involvement of quite sophisticated algorithms of high
complexity. Here we will limit our consideration by the comparative analysis almost entirely
based on the results from Section 7.1.
7.2.2 Primary Discontinuities
Table 7.1 contains the physical layout and equivalent circuit of typical planar discontinuities
and includes the coaxial discontinuities with the same or close equivalent circuit. Several
openings in this table mean there is no information, or the layout is too intricate to be fit in the
table. Apparently, the broad similarity in layout tells us about resembling in the accumulated
E- and H-field energy over the discontinuities. We assume that the reader applying this idea
will be able to expand the table to the not presented feed line like finline, etc.
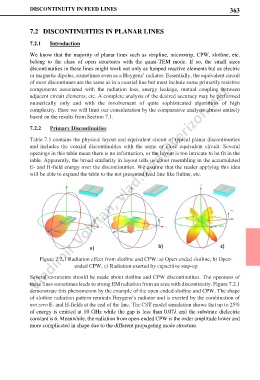
Figure 7.2.1 Radiation effect from slotline and CPW: a) Open-ended slotline, b) Open-
ended CPW, c) Radiation exerted by capacitive step-up
Several comments should be made about slotline and CPW discontinuities. The openness of
these lines sometimes leads to strong EM radiation from an area with discontinuity. Figure 7.2.1
demonstrate this phenomenon by the example of the open-ended slotline and CPW. The shape
of slotline radiation pattern reminds Huygens’s radiator and is exerted by the combination of
not zero E- and H-fields at the end of the line. The CST model simulation shows that up to 25%
of energy is emitted at 10 GHz while the gap is less than 0.07 and the substrate dielectric
constant is 6. Meanwhile, the radiation from open-ended CPW is the order amplitude lower and
more complicated in shape due to the different propagating mode structure.