Page 386 - AWSAR 2.0
P. 386
362 || AWSAR Awarded Popular Science Stories - 2019
mitochondrial superoxide dismutase and of these mitochondria targeted antioxidants in lipophilic cation tri-phenyl-phosphonium, which liver cancer were unclear during the beginning get accumulated several hundred folds in of research.
mitochondria. According to Dr Bharati, the role
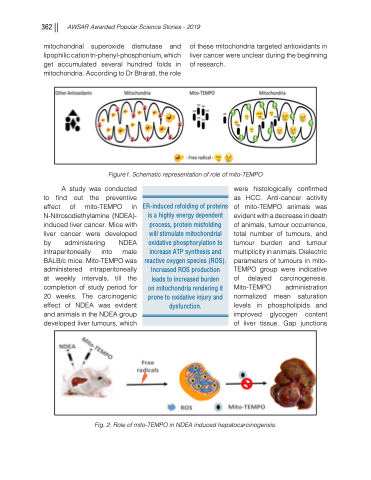
Figure1. Schematic representation of role of mito-TEMPO
A study was conducted were histologically confirmed to find out the preventive as HCC. Anti-cancer activity effect of mito-TEMPO in of mito-TEMPO animals was N-Nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA)- evident with a decrease in death induced liver cancer. Mice with of animals, tumour occurrence, liver cancer were developed total number of tumours, and by administering NDEA tumour burden and tumour intraperitoneally into male multiplicity in animals. Dielectric BALB/c mice. Mito-TEMPO was parameters of tumours in mito- administered intraperitoneally TEMPO group were indicative at weekly intervals, till the of delayed carcinogenesis. completion of study period for Mito-TEMPO administration 20 weeks. The carcinogenic normalized mean saturation effect of NDEA was evident levels in phospholipids and and animals in the NDEA group improved glycogen content developed liver tumours, which of liver tissue. Gap junctions
ER-induced refolding of proteins is a highly energy dependent process, protein misfolding will stimulate mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation to increase ATP synthesis and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Increased ROS production leads to increased burden
on mitochondria rendering it prone to oxidative injury and dysfunction.
Fig. 2. Role of mito-TEMPO in NDEA induced hepatocarcinogensis.