Page 545 - StudyBook.pdf
P. 545
Basis of Cryptography • Chapter 9 529
Data Encryption Standard
and Triple Data Encryption Standard
Among the oldest and most famous encryption algorithms is the Data Encryption
Standard (DES), the use of which has declined with the advent of algorithms that
provide improved security. DES was based on the Lucifer algorithm invented by
Horst Feistel, which never saw widespread use. Essentially, DES uses a single 64-bit
key—56 bits of data and 8 bits of parity—and operates on data in 64-bit chunks.
This key is broken into 16 48-bit subkeys, one for each round, which are called
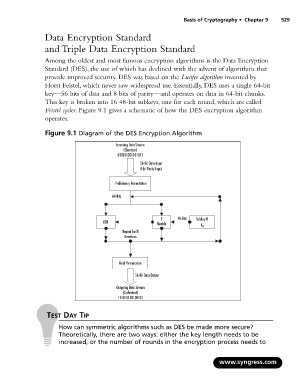
Feistel cycles. Figure 9.1 gives a schematic of how the DES encryption algorithm
operates.
Figure 9.1 Diagram of the DES Encryption Algorithm
Incoming Data Stream
(Cleartext)
010011001101011
56-Bit Data Input
8-bit Parity Input
Preliminary Permutation
64-Bits
F 48-Bits Subkey N
XOR Module
K N
Repeat for N
Iterations
Final Permutation
56-Bit Data Output
Outgoing Data Stream
(Ciphertext)
111010110100101
TEST DAY TIP
How can symmetric algorithms such as DES be made more secure?
Theoretically, there are two ways: either the key length needs to be
increased, or the number of rounds in the encryption process needs to
www.syngress.com