Page 8 - A guide to dosage form 1_full v3
P. 8
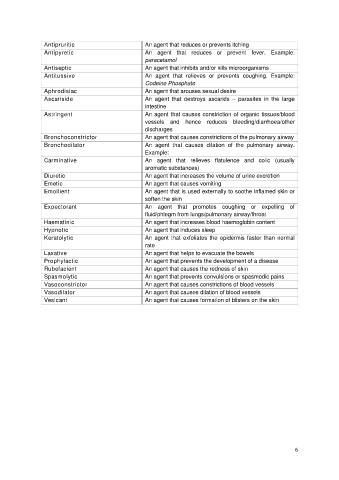
Antipruritic An agent that reduces or prevents itching
Antipyretic An agent that reduces or prevent fever. Example:
paracetamol
Antiseptic An agent that inhibits and/or kills microorganisms
Antitussive An agent that relieves or prevents coughing. Example:
Codeine Phosphate
Aphrodisiac An agent that arouses sexual desire
Ascariside An agent that destroys ascarids – parasites in the large
intestine
Astringent An agent that causes constriction of organic tissues/blood
vessels and hence reduces bleeding/diarrhoea/other
discharges
Bronchoconstrictor An agent that causes constrictions of the pulmonary airway
Bronchodilator An agent that causes dilation of the pulmonary airway.
Example:
Carminative An agent that relieves flatulence and colic (usually
aromatic substances)
Diuretic An agent that increases the volume of urine excretion
Emetic An agent that causes vomiting
Emollient An agent that is used externally to soothe inflamed skin or
soften the skin
Expectorant An agent that promotes coughing or expelling of
fluid/phlegm from lungs/pulmonary airway/throat
Haematinic An agent that increases blood haemoglobin content
Hypnotic An agent that induces sleep
Keratolytic An agent that exfoliates the epidermis faster than normal
rate
Laxative An agent that helps to evacuate the bowels
Prophylactic An agent that prevents the development of a disease
Rubefacient An agent that causes the redness of skin
Spasmolytic An agent that prevents convulsions or spasmodic pains
Vasoconstrictor An agent that causes constrictions of blood vessels
Vasodilator An agent that causes dilation of blood vessels
Vesicant An agent that causes formation of blisters on the skin
6