Page 66 - March 2020 - WT Site
P. 66
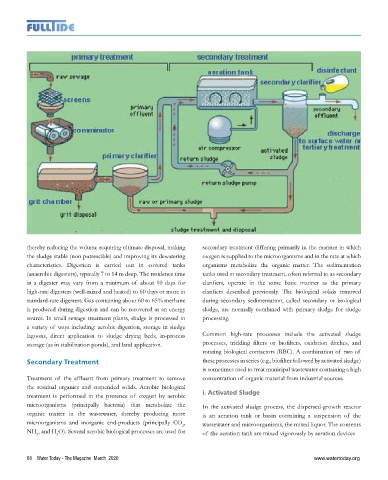
thereby reducing the volume requiring ultimate disposal, making secondary treatment differing primarily in the manner in which
the sludge stable (non putrescible) and improving its dewatering oxygen is supplied to the microorganisms and in the rate at which
characteristics. Digestion is carried out in covered tanks organisms metabolize the organic matter. The sedimentation
(anaerobic digesters), typically 7 to 14 m deep. The residence time tanks used in secondary treatment, often referred to as secondary
in a digester may vary from a minimum of about 10 days for clarifiers, operate in the same basic manner as the primary
high-rate digesters (well-mixed and heated) to 60 days or more in clarifiers described previously. The biological solids removed
standard-rate digesters. Gas containing about 60 to 65% methane during secondary sedimentation, called secondary or biological
is produced during digestion and can be recovered as an energy sludge, are normally combined with primary sludge for sludge
source. In small sewage treatment plants, sludge is processed in processing.
a variety of ways including: aerobic digestion, storage in sludge
lagoons, direct application to sludge drying beds, in-process Common high-rate processes include the activated sludge
storage (as in stabilization ponds), and land application. processes, trickling filters or biofilters, oxidation ditches, and
rotating biological contactors (RBC). A combination of two of
Secondary Treatment these processes in series (e.g., biofilter followed by activated sludge)
is sometimes used to treat municipal wastewater containing a high
Treatment of the effluent from primary treatment to remove concentration of organic material from industrial sources.
the residual organics and suspended solids. Aerobic biological
treatment is performed in the presence of oxygen by aerobic i. Activated Sludge
microorganisms (principally bacteria) that metabolize the In the activated sludge process, the dispersed-growth reactor
organic matter in the wastewater, thereby producing more is an aeration tank or basin containing a suspension of the
microorganisms and inorganic end-products (principally CO , wastewater and microorganisms, the mixed liquor. The contents
2
NH , and H O). Several aerobic biological processes are used for of the aeration tank are mixed vigorously by aeration devices
3 2
68 Water Today - The Magazine March 2020