Page 6 - Linde - LSC Linde synchron control
P. 6
06
System comparison.
The architecture.
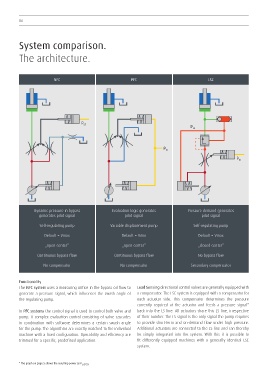
NFC PFC LSC
p
ST p
LS
p
ST
p
ST
Dynamic pressure in bypass Evaluation logic generates Pressure demand generates
generates pilot signal pilot signal pilot signal
Self-regulating pump Variable displacement pump Self-regulating pump
Default = Vmax Default = Vmin Default = Vmax
„open center“ „open center“ „closed center“
Continuous bypass flow Continuous bypass flow No bypass flow
No compensator No compensator Secondary compensator
Functionality
The NFC system uses a measuring orifice in the bypass oil flow to Load Sensing directional control valves are generally equipped with
generate a pressure signal, which influences the swash angle of a compensator. The LSC system is equipped with a compensator for
the regulating pump. each actuator side. This compensator determines the pressure
currently required at the actuator and feeds a pressure signal*
In PFC systems the control signal is used to control both valve and back into the LS line. All actuators share this LS line, irrespective
pump. A complex evaluation control consisting of valve cascades of their number. The LS signal is the only signal the pump requires
in combination with software determines a certain swash angle to provide short-term and on-demand flow under high pressure.
for the pump. The algorithms are exactly matched to the individual Additional actuators are connected to the LS line and can thereby
machine with a fixed configuration. Operability and efficiency are be simply integrated into the system. With this it is possible to
trimmed for a specific, predefined application. fit differently equipped machines with a generally identical LSC
system.
* The graph on page 5 shows the resulting power as P p(LS) .