Page 15 - Schroeder - Fuel Filtration
P. 15
Particulate Removal Element Media Selection
Considerations
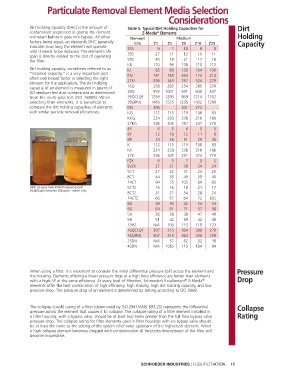
Dirt holding capacity (DHC) is the amount of Table 5. Typical Dirt Holding Capacities for Dirt
contaminant (expressed in grams) the element Z-Media Elements
®
will retain before it goes into bypass. All other Element Medium Holding
factors being equal, an element’s DHC generally Size Z1 Z3 Z5 Z10 Z25 Capacity
indicates how long the element will operate 3TA 9 7 10 8 8
until it needs to be replaced. The element’s life
span is directly related to the cost of operating 3TB 27 11 12 11 11
the filter. 5TB 40 18 21 17 18
KB 110 99 138 110 112
Dirt holding capacity, sometimes referred to as KI 85 88 130 104 106
"retained capacity," is a very important and KKI 181 185 263 174 214
often overlooked factor in selecting the right 27KI 336 345 357 324 279
element for the appli cation. The dirt holding
capacity of an element is measured in grams of 16Q 258 283 254 280 234
ISO medium test dust contaminant as determined 39Q 593 1001 691 940 537
from the multi-pass test (ISO 16889). When 39QCLQF 1259 1293 869 1214 1102
selecting filter elements, it is beneficial to 39QPML 1485 1525 1235 1432 1299
compare the dirt holding capacities of elements BBI 306 341 272
with similar particle removal efficiencies. KG 112 115 119 108 93
KKG 224 230 238 216 186
27KG 336 345 357 247 279
4Y 6 5 6 5 5
8Y 12 10 12 11 9
8R 33 26 51 29 30
K 112 115 119 108 93
KK 224 230 238 216 186
27K 336 345 357 324 279
FZX 6 5 7 5 5
SVZX 27 21 30 24 24
5CT 27 22 31 24 25
8CT 44 35 49 39 40
14CT 94 75 105 84 85
BDC: 25 gpm Fuel Filter/Coalescing Cart 5CTZ 19 16 18 21 17
25,000 ppm became 250 ppm - water only
8CTZ 31 27 34 28 24
14CTZ 66 57 64 72 60S
6G 38 30 42 34 34
9G 64 51 71 57 58
5H 26 28 39 47 48
9H 51 42 59 42 48
13HZ N/A 100 113 119 123
16QCLQF 307 315 364 306 278
16QPML 307 315 364 330 299
25DN N/A 57 62 52 48
40DN N/A 105S 115 104 94
When sizing a filter, it is important to consider the initial differential pressure (ΔP) across the element and Pressure
the housing. Elements offering a lower pressure drop at a high Beta efficiency are better than elements
®
with a high ΔP at the same efficiency. At every level of filtration, Schroeder’s Excellement Z-Media Drop
®
elements offer the best combination of high efficiency, high stability, high dirt holding capacity, and low
pressure drop. The pressure drop of an element is determined by testing according to ISO 3968.
The collapse (crush) rating of a filter (determined by ISO 2941/ANSI B93.25) represents the differential Collapse
pressure across the element that causes it to collapse. The collapse rating of a filter element installed in
a filter housing, with a bypass valve, should be at least two times greater than the full flow bypass valve Rating
pressure drop. The collapse rating for filter elements used in filter housings with no bypass valve should
be at least the same as the setting of the system relief valve upstream of the high-crush element. When
a high collapse element becomes clogged with contamination all functions downstream of the filter will
become inoperative.
SCHROEDER INDUSTRIES | FUEL FILTRATION 15