Page 8 - Parker - Vacuum products
P. 8
Catalog 0802-E Vacuum Cups
Cup Selection Technical Information
Selecting the proper vacuum cup Lifting forces
When calculating lifting forces, safety factors of 2 for
! CAUTION: horizontal lifts and 4 for vertical lifts are minimum values.
A Selecting the type of vacuum cup, material, and size Applications with irregular shapes, difficult surfaces, and
suitable for an application is important to the overall
backward motions will require increased safety factors.
vacuum system. Calculating the forces involved for each
application is recommended to determine the vacuum
cup size. It should be noted that these calculations are
basic theoretical guidelines and each application must
be tested for actual results. With all vacuum applications,
certain practical assumptions concerning cup materials,
environmental conditions, and product characteristics to
Technical
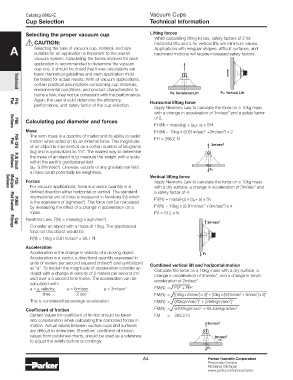
name a few, may not be consistent with the performance. FH: Horizontal Lift FV: Vertical Lift
Again, the user should determine the efficiency, Horizontal lifting force
performance, and safety factor of the cup selection.
Flat
Apply Newtons Law to calculate the force on a 10kg mass
PFG
with a change in acceleration of 3m/sec and a safety factor
2
of 2.
Calculating pad diameter and forces
FH(N) = mass(kg) x (a g+ a) x SH
PBG
Bellows
Mass FH(N) = 10kg x (9.81m/sec +3m/sec ) x 2
2
2
The term mass is a quantity of matter and its ability to resist FH = 256.2 N
motion when acted on by an external force. The magnitude
of an object is represented as a certain number of kilograms 3m/sec 2
Flat
(kg) and is symbolized as “m”. The easiest way to determine
P5V-CFS
the mass of an object is to measure the weight with a scale
within the earth’s gravitational field
(ag = 9.81m/sec ). Likewise, outside of any gravitational field, 10kg
2
Bellows
a mass could potentially be weightless. FH
PJG Short
Vertical lifting force
Forces Apply Newtons Law to calculate the force on a 10kg mass
For vacuum applications, force is a vector quantity in a with a dry surface, a change in acceleration of 3m/sec and
2
PCG
Bellows
Multiple
defined direction either horizontal or vertical. The standard a safety factor of 4.
international unit of force is measured in Newtons (N) which FV(N) = mass(kg) x (a g+ a) x Sv
is the equivalent of (kgm/sec ). The force can be calculated
2
2
2
by measuring the effect of a change in acceleration on a FV(N) = 10kg x (9.81m/sec +3m/sec ) x 4
PUGB
mass. FV = 512.4 N
Flat Swivel
2
Newtons Law: F(N) = mass(kg) x ag(m/sec )
3m/sec 2
Consider an object with a mass of 10kg. The gravitational
Cup
Fittings
force on this object would be:
F(N) = 10kg x 9.81m/sec = 98.1 N 10kg
2
Acceleration
Acceleration is the change in velocity of a moving object. FV
Acceleration is a vector, a directional quantity expressed in
units of meters per second squared (m/sec ) and symbolized Combined vertical lift and horizontal motion
2
as “a”. To explain the magnitude of acceleration consider an Calculate the force on a 10kg mass with a dry surface, a
object with a change in velocity of 2 meters per second (m/ change in acceleration of 3m/sec , and a change in travel
2
sec) over a 4 second time frame. The acceleration can be acceleration of 2m/sec .
2
calculated with:
2
a = velocity a = 6m/sec a = 3m/sec 2 FM(N) = FV + FH 2
time 2 sec FM(N) = [(10kg x 2m/sec ) x 4] + [10kg x (9.81m/sec + 3m/sec ) x 2] 2
2
2
2
2
This is considered an average acceleration. FM(N) = (80kgm/sec ) + [256kgm/sec ]
2 2
2 2
2
Coefficient of friction FM(N) = 6400kgm/sec + 65,536kgm/sec 2
Certain values for coefficient of friction should be taken FM = 268.2 N
into consideration when calculating the combined forces in
motion. Actual values between suction cups and surfaces 3m/sec 2
are difficult to determine. Therefore, coefficient of friction
values from published charts, should be used as a reference 2m/sec 2
to adjust the safety factors accordingly.
10kg
FH
A4 Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics