Page 108 - Pharmaceutical Organic Chemmistry-3 (Theoritical book) 24-25
P. 108
Clinical Pharmacy PharmD - 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-3 (PC 305)
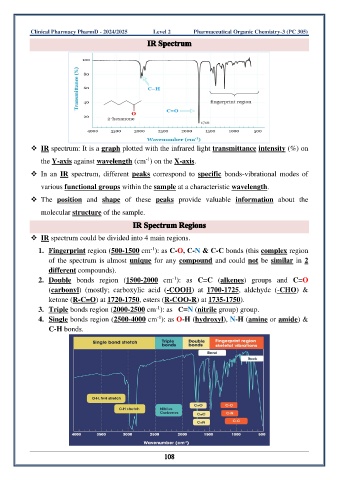
❖ IR spectrum: It is a graph plotted with the infrared light transmittance intensity (%) on
-1
the Y-axis against wavelength (cm ) on the X-axis.
❖ In an IR spectrum, different peaks correspond to specific bonds-vibrational modes of
various functional groups within the sample at a characteristic wavelength.
❖ The position and shape of these peaks provide valuable information about the
molecular structure of the sample.
❖ IR spectrum could be divided into 4 main regions.
1. Fingerprint region (500-1500 cm ): as C-O, C-N & C-C bonds (this complex region
-1
of the spectrum is almost unique for any compound and could not be similar in 2
different compounds).
-1
2. Double bonds region (1500-2000 cm ): as C=C (alkenes) groups and C=O
(carbonyl) (mostly; carboxylic acid (-COOH) at 1700-1725, aldehyde (-CHO) &
ketone (R-C=O) at 1720-1750, esters (R-COO-R) at 1735-1750).
-1
3. Triple bonds region (2000-2500 cm ): as C≡N (nitrile group) group.
-1
4. Single bonds region (2500-4000 cm ): as O-H (hydroxyl), N-H (amine or amide) &
C-H bonds.