Page 4 - Extraction and filtration technology for solder fumes and vapors_NA
P. 4
Health risks and
legal basis
In North America, the primary federal agency responsible These regulations often differentiate between substanc-
for workplace air quality is the Occupational Safety and es based on their health risks, such as whether they
Health Administration (OSHA). OSHA sets standards for harm the brain, nerves, or respiratory system, and wheth-
permissible exposure limits (PELs) for various airborne er they can be inhaled deeply into the lungs.
contaminants. Additionally, the National Institute for
Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends It’s essential for businesses to comply with all applicable
exposure limits (RELs) that are often more protective regulations to protect worker health and safety.
than PELs.
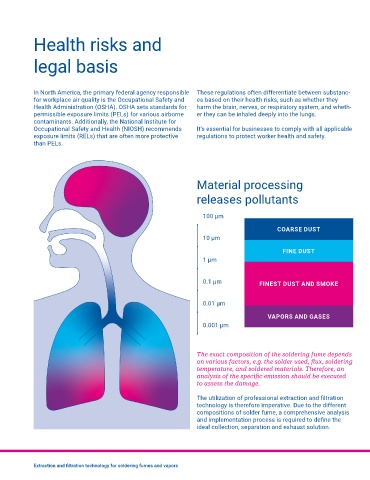
Material processing
releases pollutants
100 μm
COARSE DUST
10 μm
FINE DUST
1 μm
0.1 μm FINEST DUST AND SMOKE
0.01 μm
VAPORS AND GASES
0.001 μm
The exact composition of the soldering fume depends
on various factors, e.g. the solder used, flux, soldering
temperature, and soldered materials. Therefore, an
analysis of the specific emission should be executed
to assess the damage.
The utilization of professional extraction and filtration
technology is therefore imperative. Due to the different
compositions of solder fume, a comprehensive analysis
and implementation process is required to define the
ideal collection, separation and exhaust solution.
Extraction and filtration technology for soldering fumes and vapors 5