Page 90 - Ripples SCIENCE 7 - TEJPUR Edition 2024 Answer Key
P. 90
8. What is the mechanism of breathing in cockroaches and earthworms?
Ans. Breathing in cockroaches : Cockroaches have tiny holes present on both the sides of
their bodies. These tiny holes are called spiracles. Also, they have air tubes called the
tracheae that allows the exchange of gases within their body. The air enters the body
through the spiracles and diffuses in to the cells via network of tracheae.
Breathing in earthworms : Earthworms have a soft, slimy and moist skin. Gases can
easily pass in and out of an earthworm’s body through its skin.
9. Why we must breathe through our nose and not through our mouth?
Ans. Breathing through our nose filters warms and humidifies air as tiny hair and mucus
are present in the nostrils. These help protect our lungs. Breathing through mouth
may affect our lungs as tiny hair & mucus are not present there.
G. Long-answer questions.
1. Smoking is harmful to health. Explain in brief.
Ans. Smoking can cause lung diseases by damaging the airways and the small air sacs found
in the lungs. It also results in accumulation of tar in lungs. It narrows the bronchi and
bronchioles which may lead to ‘bronchitis’, a condition in which a person is unable
to breathe with ease. Too much smoking may result in lung cancer and many other
health issues.
2. How do the plants respire? Explain.
Ans. Respiration in Plants
All plant cells require energy for activities, such as synthesis of proteins from amino
acids, making starch from glucose, absorbing minerals from the soil etc. Plants get
this energy through the process of respiration, in which glucose is broken down into
carbon dioxide and water along with the release of energy.
All parts in a plant respire independently. During respiration, they take in oxygen and
give out carbon dioxide. In the leaves and green stems, the exchange of gases during
respiration take place through the stomata (singular stoma), which are tiny pores on
the leaves, and in stems through minute permanent openings called lenticels.
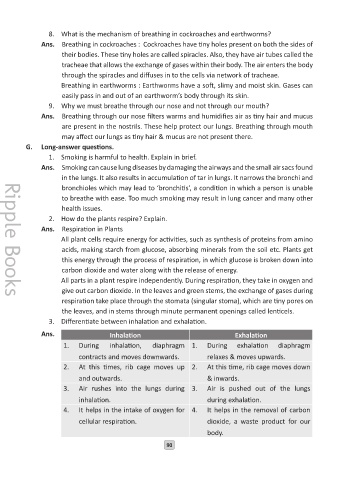
3. Differentiate between inhalation and exhalation.
Ans. Inhalation Exhalation
1. During inhalation, diaphragm 1. During exhalation diaphragm
contracts and moves downwards. relaxes & moves upwards.
2. At this times, rib cage moves up 2. At this time, rib cage moves down
and outwards. & inwards.
3. Air rushes into the lungs during 3. Air is pushed out of the lungs
inhalation. during exhalation.
4. It helps in the intake of oxygen for 4. It helps in the removal of carbon
cellular respiration. dioxide, a waste product for our
body.
90