Page 228 - Industrial Tools Catalog (1)
P. 228
Thread tools \ Technical introduction – thread forming
Thread forming — the process
Process:
In contrast to tapping, where sections are cut out of the material, thread forming is a non-cutting, pressure forming procedure.
Advantages:
No chip formation
Up to 30% higher surface quality than with thread cutting
Up to 40% higher processing speed than with thread cutting
Threads in through holes and blind holes can be produced with the same tool
Wide range of materials processable
Cutting of thread eliminated
Thread pitch and thread angle errors as with cut threads eliminated
Shaped threads have higher strength owing to non-continuous cut
Requirements: For all shapeable materials with elongation >10 %.
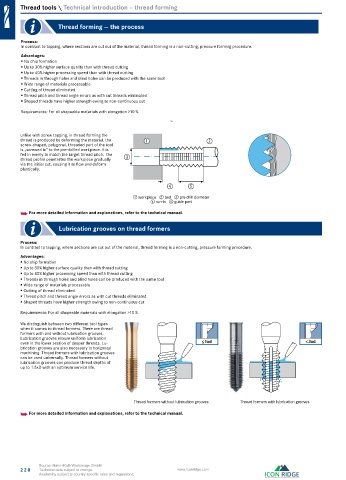
unlike with screw tapping, in thread forming the
thread is produced by deforming the material. the 1 2
screw-shaped, polygonal, threaded part of the tool
is „screwed in“ to the pre-drilled workpiece. It is
fed in evenly to match the target thread pitch. the
thread profile penetrates the workpiece gradually 3
via the initial cut, causing it to flow and deform
plastically.
4 5
① workpiece ② tool ③ pre-drill diameter
④ run-in ⑤ guide part
h For more detailed information and explanations, refer to the technical manual.
Lubrication grooves on thread formers
Process:
In contrast to tapping, where sections are cut out of the material, thread forming is a non-cutting, pressure forming procedure.
Advantages:
No chip formation
Up to 30% higher surface quality than with thread cutting
Up to 40% higher processing speed than with thread cutting
Threads in through holes and blind holes can be produced with the same tool
Wide range of materials processable
Cutting of thread eliminated
Thread pitch and thread angle errors as with cut threads eliminated
Shaped threads have higher strength owing to non-continuous cut
Requirements: For all shapeable materials with elongation >10 %.
We distinguish between two different tool types
when it comes to thread formers. There are thread
formers with and without lubrication grooves.
Lubrication grooves ensure uniform lubrication 3xd
even in the lower section of deeper threads. Lu- 1xd
brication grooves are also necessary in horizontal
machining. Thread formers with lubrication grooves
can be used universally. Thread formers without
lubrication grooves can produce thread depths of
up to 1.5xD with an optimum service life.
Thread formers without lubrication grooves Thread formers with lubrication grooves
h For more detailed information and explanations, refer to the technical manual.
Source: Hahn+Kolb Werkzeuge GmbH
228 Technical data subject to change. www.iconridge.com
Availability subject to country specific rules and regulations.