Page 70 - CPG - Clinical Practice Guidelines - Management of Cancer Pain
P. 70
A Ask the child and Assess pain score
A
Ask the child and Assess pain score
B Use Behavioural and Biological measures
Use Behavioural and Biological measures
B
C Find the Cause
Find the Cause
C
D Decide and Deliver treatment in a timely manner
Management of Cancer Pain (Second Edition)
Decide and Deliver treatment in a timely manner
D
E Evaluate outcome
E
Evaluate outcome
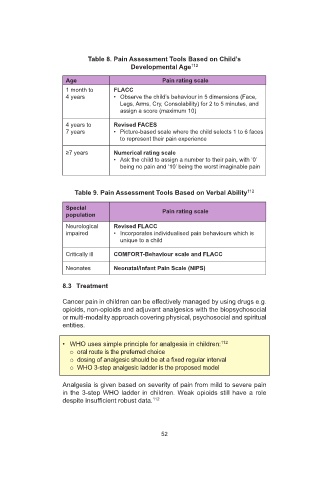
7DEOH 3DLQ $VVHVVPHQW 7RROV %DVHG RQ &KLOG¶V
Developmental Age 112
Age Pain rating scale
Pain rating scale
Age
1 month to FLACC
1 month to
FLACC
4 years • Observe the child’s behaviour in 5 dimensions (Face,
• Observe the child’s behaviour in 5 dimensions (Face,
4 years
Legs, Arms, Cry, Consolability) for 2 to 5 minutes, and
Legs, Arms, Cry, Consolability) for 2 to 5 minutes, and
assign a score (maximum 10)
assign a score (maximum 10)
4 years to Revised FACES
4 years to
Revised FACES
7 years • Picture-based scale where the child selects 1 to 6 faces
7 years
• Picture-based scale where the child selects 1 to 6 faces
to represent their pain experience
to represent their pain experience
\HDUV Numerical rating scale
\HDUV
Numerical rating scale
• Ask the child to assign a number to their pain, with ‘0’
• Ask the child to assign a number to their pain, with ‘0’
being no pain and ‘10’ being the worst imaginable pain
being no pain and ‘10’ being the worst imaginable pain
7DEOH 3DLQ $VVHVVPHQW 7RROV %DVHG RQ 9HUEDO $ELOLW\ 112
Special Pain rating scale
Special
population Pain rating scale
population
Neurological Revised FLACC
Revised FLACC
Neurological
impaired • Incorporates individualised pain behaviours which is
• Incorporates individualised pain behaviours which is
impaired
unique to a child
unique to a child
Critically ill COMFORT-Behaviour scale and FLACC
COMFORT-Behaviour scale and FLACC
Critically ill
Neonates Neonatal/Infant Pain Scale (NIPS)
Neonatal/Infant Pain Scale (NIPS)
Neonates
7UHDWPHQW
Cancer pain in children can be effectively managed by using drugs e.g.
opioids, non-opioids and adjuvant analgesics with the biopsychosocial
or multi-modality approach covering physical, psychosocial and spiritual
entities.
• WHO uses simple principle for analgesia in children: 112
{ oral route is the preferred choice
{ GRVLQJ RI DQDOJHVLF VKRXOG EH DW D ¿[HG UHJXODU LQWHUYDO
{ WHO 3-step analgesic ladder is the proposed model
Analgesia is given based on severity of pain from mild to severe pain
in the 3-step WHO ladder in children. Weak opioids still have a role
GHVSLWH LQVXI¿FLHQW UREXVW GDWD 112
52
e-cpg inside text-Cancer pain-25/5/24.indd 52 09/08/2024 12:09 AM