Page 159 - W01TB8_2017-18_[low-res]_F2F_Neat
P. 159
Chapter 10 Ethics, corporate governance and internal controls 10/7
Risk management provides a link between the ongoing operational management of risk and longer-term
business goals and strategies. Appropriate risk management policies should be set by each insurer
according to the nature, scale and complexity of its business.
It is usual to identify risk at three levels:
• Internal: the impact of the risk absent of any controls.
• Appetite (tolerance): the impact of the risk the insurer is prepared to accept.
• Residual; the impact of the risk after applying mitigation controls.
The level of impact is a combination of frequency and severity. Residual risk should always be at, or
lower, than appetite (tolerance) otherwise the controls are not effective.
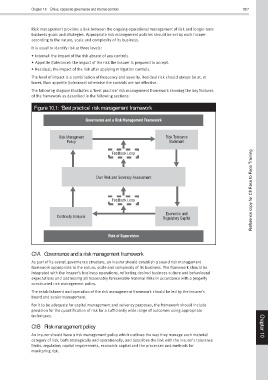
The following diagram illustrates a ‘best practice’ risk management framework showing the key features
of the framework as described in the following sections:
Figure 10.1: ‘Best practice’ risk management framework
Governance and a Risk Management Framework
Risk Managment Risk Tolerance
Policy Statement
Feedback Loop
Own Risk and Solvency Assessment
Feedback Loop Reference copy for CII Face to Face Training
Economic and
Continuity Analysis Regulatory Capital
Role of Supervision
C1A Governance and a risk management framework
As part of its overall governance structure, an insurer should establish a sound risk management
framework appropriate to the nature, scale and complexity of its business. The framework should be
integrated with the insurer’s business operations, reflecting desired business culture and behavioural
expectations and addressing all reasonably foreseeable material risks in accordance with a properly
constructed risk management policy.
The establishment and operation of the risk management framework should be led by the insurer’s
board and senior management.
For it to be adequate for capital management and solvency purposes, the framework should include
provision for the quantification of risk for a sufficiently wide range of outcomes using appropriate
techniques.
C1B Risk management policy Chapter
An insurer should have a risk management policy which outlines the way they manage each material 10
category of risk, both strategically and operationally, and describes the link with the insurer’s tolerance
limits, regulatory capital requirements, economic capital and the processes and methods for
monitoring risk.