Page 91 - M97TB9_2018-19_[low-res]_F2F_Neat2
P. 91
Chapter 4 Features and operation of proportional reinsurance treaties 4/19
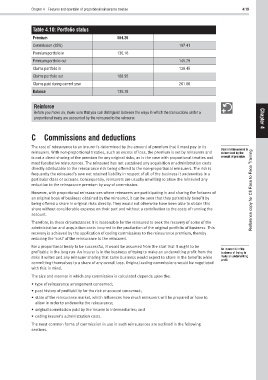
Table 4.10: Portfolio status
Premium 564.26
Commission (35%) 197.41
Premium portfolio in 130.16
Premium portfolio out 145.79
Claims portfolio in 138.45
Claims portfolio out 188.95
Claims paid during current year 261.86
Balance 139.78
Reinforce
Before you move on, make sure that you can distinguish between the ways in which the transactions under a
proportional treaty are accounted by the reinsured to the reinsurer. Chapter
4
C Commissions and deductions
The cost of reinsurance to an insurer is determined by the amount of premium that it must pay to its
Cost of reinsurance is
reinsurers. With non-proportional treaties, such as excess of loss, the premium is set by reinsurers and determined by the
is not a direct sharing of the premium for any original risks, as is the case with proportional treaties and amount of premium
most facultative reinsurances. The reinsured has not sustained any acquisition or administration costs
directly attributable to the reinsurance risk being offered to the non-proportional reinsurers. The risk is
frequently the reinsured’s own net retained liability in respect of all of the business it underwrites in a
particular class or account. Consequently, reinsurers are usually unwilling to allow the reinsured any
reduction in the reinsurance premium by way of commission.
However, with proportional reinsurances where reinsurers are participating in and sharing the fortunes of Reference copy for CII Face to Face Training
an original book of business obtained by the reinsured, it can be seen that they potentially benefit by
being offered a share in original risks directly. They would not otherwise have been able to obtain this
share without considerable expense on their part and without a contribution to the costs of running the
account.
Therefore, in these circumstances it is reasonable for the reinsured to seek the recovery of some of the
administration and acquisition costs incurred in the production of the original portfolio of business. This
recovery is achieved by the application of ceding commissions to the reinsurance premium, thereby
reducing the ‘cost’ of the reinsurance to the reinsured.
For a proportional treaty to be successful, it would be assumed from the start that it ought to be
An insurer is in the
profitable in the long run. An insurer is in the business of trying to make an underwriting profit from the business of trying to
risks it writes and any reinsurer sharing that same business would expect to share in the benefits while make an underwriting
profit
committing themselves to a share of any overall loss. Original ceding commissions would be negotiated
with this in mind.
The size and manner in which any commission is calculated depends upon the:
• type of reinsurance arrangement concerned;
• past history of profitability for the risk or account concerned;
• state of the reinsurance market, which influences how much reinsurers will be prepared or have to
allow in order to underwrite the reinsurance;
• original commission paid by the insurer to intermediaries; and
• ceding insurer’s administration costs.
The most common forms of commission in use in such reinsurances are outlined in the following
sections.