Page 2 - PDTrac Tech Overview
P. 2
ON-LINE MONITORING THE EFFICIENT WAY
The What?
The What … Partial Discharge
… because the PD monitoring system uses VHF and time-of-flight to automatically filter out noise and classify disturbances, then the output of the PDTrac
monitor is only the PD detected by each sensor. As such, the DCS can be configured to trend (doubling over a twelve-month interval) and when compared
to the Iris database issue alerts, warnings, and notifications. Additionally, the polarity of the PD pulses is tracked individually, so whether the source is
polarity predominant and/or correlates with load or temperature can be determined. This makes it possible to determine the problem coils and if the
problems are likely due to thermal deterioration, coil/bar movement, surface activity or deterioration of the turn insulation.
400
High 217-360mV
350
300
Peak Magnitude (mV) 250 C1 Qm+
200
C1 Qm-
150
Linear (C1 Qm+)
100
Moderate 62-316mV Linear (C1 Qm-)
50
Typical <62mV
0
9/15 10/15 11/15 12/15 1/16 2/16 3/16 4/16 5/16 6/16 7/16 8/16 9/16 10/16
Month/Year
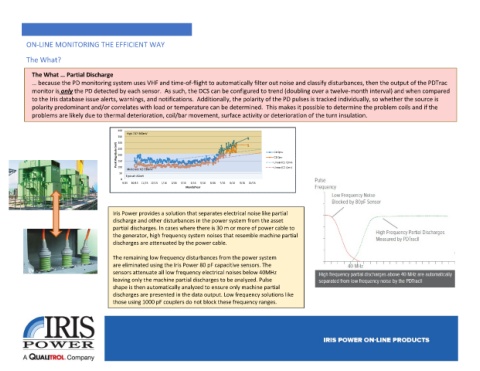
Iris Power provides a solution that separates electrical noise like partial
discharge and other disturbances in the power system from the asset
partial discharges. In cases where there is 30 m or more of power cable to
the generator, high frequency system noises that resemble machine partial
discharges are attenuated by the power cable.
The remaining low frequency disturbances from the power system
are eliminated using the Iris Power 80 pF capacitive sensors. The
sensors attenuate all low frequency electrical noises below 40MHz
leaving only the machine partial discharges to be analyzed. Pulse
shape is then automatically analyzed to ensure only machine partial
discharges are presented in the data output. Low frequency solutions like
those using 1000 pF couplers do not block these frequency ranges.