Page 22 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 22
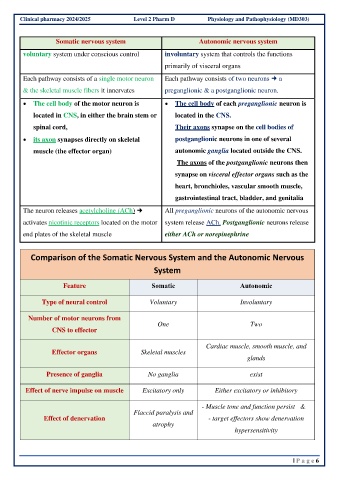
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system
voluntary system under conscious control involuntary system that controls the functions
primarily of visceral organs
Each pathway consists of a single motor neuron Each pathway consists of two neurons a
& the skeletal muscle fibers it innervates preganglionic & a postganglionic neuron.
• The cell body of the motor neuron is • The cell body of each preganglionic neuron is
located in CNS, in either the brain stem or located in the CNS.
spinal cord, Their axons synapse on the cell bodies of
• its axon synapses directly on skeletal postganglionic neurons in one of several
muscle (the effector organ) autonomic ganglia located outside the CNS.
The axons of the postganglionic neurons then
synapse on visceral effector organs such as the
heart, bronchioles, vascular smooth muscle,
gastrointestinal tract, bladder, and genitalia
The neuron releases acetylcholine (ACh) All preganglionic neurons of the autonomic nervous
activates nicotinic receptors located on the motor system release ACh. Postganglionic neurons release
end plates of the skeletal muscle either ACh or norepinephrine
Comparison of the Somatic Nervous System and the Autonomic Nervous
System
Feature Somatic Autonomic
Type of neural control Voluntary Involuntary
Number of motor neurons from
One Two
CNS to effector
Cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and
Effector organs Skeletal muscles
glands
Presence of ganglia No ganglia exist
Effect of nerve impulse on muscle Excitatory only Either excitatory or inhibitory
- Muscle tone and function persist &
Flaccid paralysis and
Effect of denervation - target effectors show denervation
atrophy
hypersensitivity
| P a g e 6