Page 66 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 66
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
Resting Membrane Potential
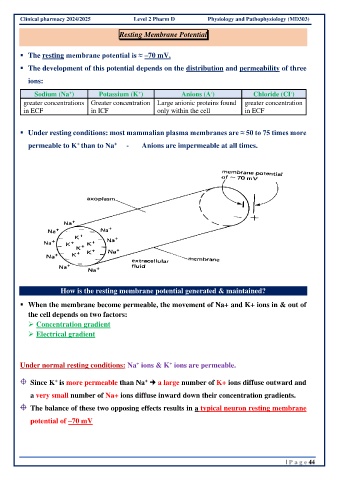
▪ The resting membrane potential is ≈ –70 mV.
▪ The development of this potential depends on the distribution and permeability of three
ions:
-
Sodium (Na ) Potassium (K ) Anions (A ) Chloride (CI )
-
+
+
greater concentrations Greater concentration Large anionic proteins found greater concentration
in ECF in ICF only within the cell in ECF
▪ Under resting conditions: most mammalian plasma membranes are ≈ 50 to 75 times more
+
+
permeable to K than to Na - Anions are impermeable at all times.
How is the resting membrane potential generated & maintained?
▪ When the membrane become permeable, the movement of Na+ and K+ ions in & out of
the cell depends on two factors:
➢ Concentration gradient
➢ Electrical gradient
Under normal resting conditions: Na ions & K ions are permeable.
+
+
+
+
Since K is more permeable than Na a large number of K+ ions diffuse outward and
a very small number of Na+ ions diffuse inward down their concentration gradients.
The balance of these two opposing effects results in a typical neuron resting membrane
potential of –70 mV
| P a g e 44