Page 44 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 44
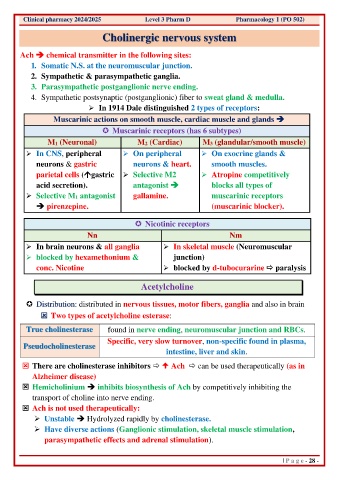
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
Cholinergic nervous system
Ach ➔ chemical transmitter in the following sites:
1. Somatic N.S. at the neuromuscular junction.
2. Sympathetic & parasympathetic ganglia.
3. Parasympathetic postganglionic nerve ending.
4. Sympathetic postsynaptic (postganglionic) fiber to sweat gland & medulla.
➢ In 1914 Dale distinguished 2 types of receptors:
Muscarinic actions on smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands ➔
Muscarinic receptors (has 6 subtypes)
M1 (Neuronal) M2 (Cardiac) M3 (glandular/smooth muscle)
➢ In CNS, peripheral ➢ On peripheral ➢ On exocrine glands &
neurons & gastric neurons & heart. smooth muscles.
parietal cells (gastric ➢ Selective M2 ➢ Atropine competitively
acid secretion). antagonist ➔ blocks all types of
➢ Selective M1 antagonist gallamine. muscarinic receptors
➔ pirenzepine. (muscarinic blocker).
Nicotinic receptors
Nn Nm
➢ In brain neurons & all ganglia ➢ In skeletal muscle (Neuromuscular
➢ blocked by hexamethonium & junction)
conc. Nicotine ➢ blocked by d-tubocurarine paralysis
Acetylcholine
Distribution: distributed in nervous tissues, motor fibers, ganglia and also in brain
Two types of acetylcholine esterase:
True cholinesterase found in nerve ending, neuromuscular junction and RBCs.
Specific, very slow turnover, non-specific found in plasma,
Pseudocholinesterase
intestine, liver and skin.
There are cholinesterase inhibitors Ach can be used therapeutically (as in
Alzheimer disease)
Hemicholinium ➔ inhibits biosynthesis of Ach by competitively inhibiting the
transport of choline into nerve ending.
Ach is not used therapeutically:
➢ Unstable ➔ Hydrolyzed rapidly by cholinesterase.
➢ Have diverse actions (Ganglionic stimulation, skeletal muscle stimulation,
parasympathetic effects and adrenal stimulation).
| P a g e - 28 -