Page 39 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 39
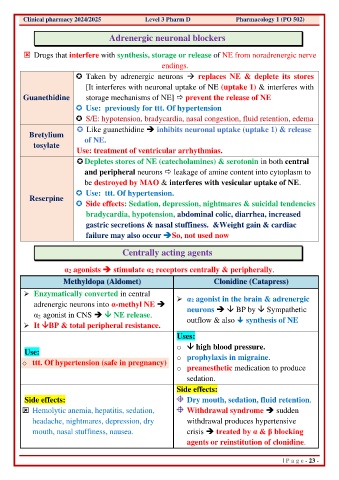
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
Adrenergic neuronal blockers
Drugs that interfere with synthesis, storage or release of NE from noradrenergic nerve
endings.
Taken by adrenergic neurons → replaces NE & deplete its stores
[It interferes with neuronal uptake of NE (uptake 1) & interferes with
Guanethidine storage mechanisms of NE] prevent the release of NE
Use: previously for ttt. Of hypertension
S/E: hypotension, bradycardia, nasal congestion, fluid retention, edema
Like guanethidine ➔ inhibits neuronal uptake (uptake 1) & release
Bretylium
tosylate of NE.
Use: treatment of ventricular arrhythmias.
Depletes stores of NE (catecholamines) & serotonin in both central
and peripheral neurons leakage of amine content into cytoplasm to
be destroyed by MAO & interferes with vesicular uptake of NE.
Use: ttt. Of hypertension.
Reserpine
Side effects: Sedation, depression, nightmares & suicidal tendencies
bradycardia, hypotension, abdominal colic, diarrhea, increased
gastric secretions & nasal stuffiness. &Weight gain & cardiac
failure may also occur ➔So, not used now
Centrally acting agents
α2 agonists ➔ stimulate α2 receptors centrally & peripherally.
Methyldopa (Aldomet) Clonidine (Catapress)
➢ Enzymatically converted in central ➢ α2 agonist in the brain & adrenergic
adrenergic neurons into α-methyl NE ➔ neurons ➔ BP by Sympathetic
α 2 agonist in CNS ➔ NE release.
➢ It BP & total peripheral resistance. outflow & also synthesis of NE
Uses:
o high blood pressure.
Use:
o ttt. Of hypertension (safe in pregnancy) o prophylaxis in migraine.
o preanesthetic medication to produce
sedation.
Side effects:
Side effects: Dry mouth, sedation, fluid retention.
Hemolytic anemia, hepatitis, sedation, Withdrawal syndrome ➔ sudden
headache, nightmares, depression, dry withdrawal produces hypertensive
mouth, nasal stuffiness, nausea. crisis ➔ treated by α & β blocking
agents or reinstitution of clonidine.
| P a g e - 23 -