Page 34 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 34
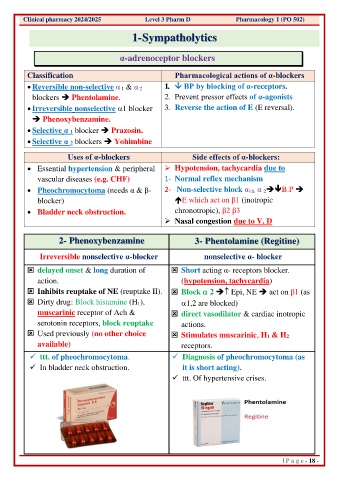
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
1- Sympatholytics
α-adrenoceptor blockers
Classification Pharmacological actions of α-blockers
• Reversible non-selective α 1 & α 2 1. BP by blocking of α-receptors.
blockers ➔ Phentolamine. 2. Prevent pressor effects of α-agonists
• Irreversible nonselective 1 blocker 3. Reverse the action of E (E reversal).
➔ Phenoxybenzamine.
• Selective α 1 blocker ➔ Prazosin.
• Selective α 2 blockers ➔ Yohimbine
Uses of α-blockers Side effects of α-blockers:
• Essential hypertension & peripheral ➢ Hypotension, tachycardia due to
vascular diseases (e.g. CHF) 1- Normal reflex mechanism
• Pheochromocytoma (needs α & β- 2- Non-selective block α 1& α 2➔B.P ➔
blocker) E which act on β1 (inotropic
• Bladder neck obstruction. chronotropic), β2 β3
➢ Nasal congestion due to V. D
2- Phenoxybenzamine 3- Phentolamine (Regitine)
Irreversible nonselective α-blocker nonselective α- blocker
delayed onset & long duration of Short acting α- receptors blocker.
action. (hypotension, tachycardia)
Inhibits reuptake of NE (reuptake II). Block 2 ➔ Epi, NE ➔ act on β1 (as
Dirty drug: Block histamine (H 1), 1,2 are blocked)
muscarinic receptor of Ach & direct vasodilator & cardiac inotropic
serotonin receptors, block reuptake actions.
Used previously (no other choice Stimulates muscarinic, H1 & H2
available) receptors.
✓ ttt. of pheochromocytoma. ✓ Diagnosis of pheochromocytoma (as
✓ In bladder neck obstruction. it is short acting).
✓ ttt. Of hypertensive crises.
| P a g e - 18 -