Page 2 - D
P. 2
Ch.1
Shape Of The Earth In Geodesy
In this chapter you will learn about scale, geodesy and coordinate systems. The chapter
will have examples and information about the aspects that make up coordinate systems.
You will learn about the determining factors to consider when creating map
projections, deformation and distribution of the projection, and how to determine
which map projection to use for a project.
What is Geodesy?
Geodesy is the scientific discipline that deals with the measurement representation of
the earth. Geodesists study the Earth’s gravitational field, motion of the Earth’s crust,
tides, and the Earth’s rotation. In order to do this, geodesists have built national control
networks that allow them to define and assign coordinates to physical locations on
earth.
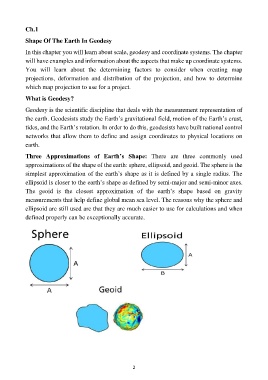
Three Approximations of Earth’s Shape: There are three commonly used
approximations of the shape of the earth: sphere, ellipsoid, and geoid. The sphere is the
simplest approximation of the earth’s shape as it is defined by a single radius. The
ellipsoid is closer to the earth’s shape as defined by semi-major and semi-minor axes.
The geoid is the closest approximation of the earth’s shape based on gravity
measurements that help define global mean sea level. The reasons why the sphere and
ellipsoid are still used are that they are much easier to use for calculations and when
defined properly can be exceptionally accurate.
2