Page 79 - phytochemistry general program
P. 79
It is still being used as well as its dihydro-derivative for the treatment of migraine
as they constrict blood vessels and also as oxytocic agent.
General Characters and stability:
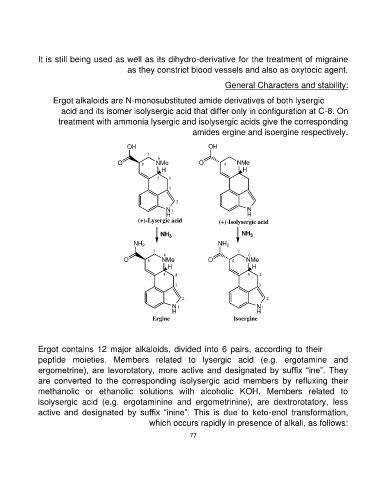
Ergot alkaloids are N-monosubstituted amide derivatives of both lysergic
acid and its isomer isolysergic acid that differ only in configuration at C-8. On
treatment with ammonia lysergic and isolysergic acids give the corresponding
amides ergine and isoergine respectively.
OH 6 OH
7 NMe O 8 NMe
H H
O8
54
3
2 N
H
N1 (+)-Isolysergic acid
H
(+)-Lysergic acid
NH3 NH3
NH2 6 NH2 6
7 NMe 7 NMe
H H
O8 O8
54 54
3 3
2 2
N1 N1
H H
Ergine Isoergine
Ergot contains 12 major alkaloids, divided into 6 pairs, according to their
peptide moieties. Members related to lysergic acid (e.g. ergotamine and
ergometrine), are levorotatory, more active and designated by suffix “ine”. They
are converted to the corresponding isolysergic acid members by refluxing their
methanolic or ethanolic solutions with alcoholic KOH. Members related to
isolysergic acid (e.g. ergotaminine and ergometrinine), are dextrorotatory, less
active and designated by suffix “inine”. This is due to keto-enol transformation,
which occurs rapidly in presence of alkali, as follows:
77