Page 85 - phytochemistry general program
P. 85
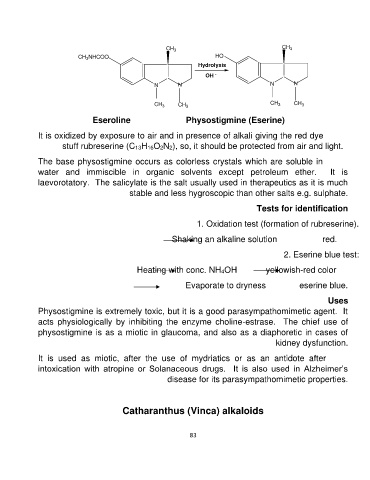
CH3NHCOO CH3 HO CH3
NN Hydrolysis NN
OH -
CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3
Eseroline Physostigmine (Eserine)
It is oxidized by exposure to air and in presence of alkali giving the red dye
stuff rubreserine (C13H16O2N2), so, it should be protected from air and light.
The base physostigmine occurs as colorless crystals which are soluble in
water and immiscible in organic solvents except petroleum ether. It is
laevorotatory. The salicylate is the salt usually used in therapeutics as it is much
stable and less hygroscopic than other salts e.g. sulphate.
Tests for identification
1. Oxidation test (formation of rubreserine).
Shaking an alkaline solution red.
2. Eserine blue test:
Heating with conc. NH4OH yellowish-red color
Evaporate to dryness eserine blue.
Uses
Physostigmine is extremely toxic, but it is a good parasympathomimetic agent. It
acts physiologically by inhibiting the enzyme choline-estrase. The chief use of
physostigmine is as a miotic in glaucoma, and also as a diaphoretic in cases of
kidney dysfunction.
It is used as miotic, after the use of mydriatics or as an antidote after
intoxication with atropine or Solanaceous drugs. It is also used in Alzheimer’s
disease for its parasympathomimetic properties.
Catharanthus (Vinca) alkaloids
83