Page 87 - phytochemistry general program
P. 87
Cell culture and organ cultures have been attempted, with considerable
success in producing the oncolytic dimeric alkaloid, but in a yield that was still less
.than that from the crud drug
It contains about 90 alkaloids, the most important are vinblastine and
vincristine. These are present in very minute amounts in the plant but are known to
have antineoplastic (cytotoxic) activity.
indole or indoline derivatives. They are alkaloids are Chemically, vinca
classified into two main groups:
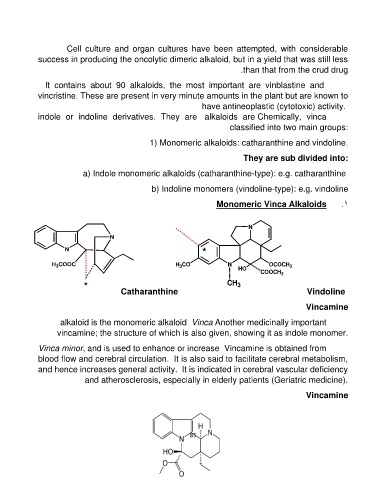
1) Monomeric alkaloids: catharanthine and vindoline.
They are sub divided into:
a) Indole monomeric alkaloids (catharanthine-type): e.g. catharanthine
b) Indoline monomers (vindoline-type): e.g. vindoline
Monomeric Vinca Alkaloids .1
N
N
N *
H3COOC
H3CO N OCOCH3
* HO COOCH3
Catharanthine CH3 Vindoline
Vincamine
alkaloid is the monomeric alkaloid Vinca Another medicinally important
vincamine; the structure of which is also given, showing it as indole monomer.
Vinca minor, and is used to enhance or increase Vincamine is obtained from
blood flow and cerebral circulation. It is also said to facilitate cerebral metabolism,
and hence increases general activity. It is indicated in cerebral vascular deficiency
and atherosclerosis, especially in elderly patients (Geriatric medicine).
Vincamine
85