Page 92 - phytochemistry general program
P. 92
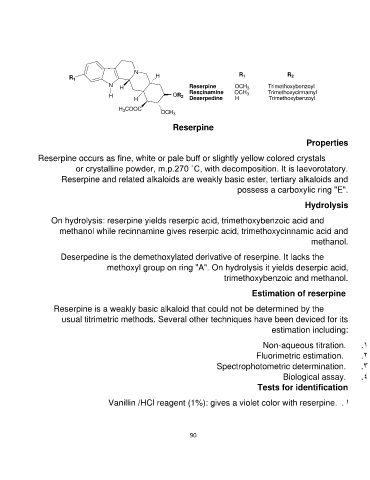
N R1 R2
R1 H
NH Reserpine OCH3 Trimethoxybenzoyl
H OCH3 Trimethoxycinnamyl
H OR2 Rescinamine H Trimethoxybenzoyl
Deserpedine
H3COOC OCH3
Reserpine
Properties
Reserpine occurs as fine, white or pale buff or slightly yellow colored crystals
or crystalline powder, m.p.270 ˚C, with decomposition. It is laevorotatory.
Reserpine and related alkaloids are weakly basic ester, tertiary alkaloids and
possess a carboxylic ring "E".
Hydrolysis
On hydrolysis: reserpine yields reserpic acid, trimethoxybenzoic acid and
methanol while recinnamine gives reserpic acid, trimethoxycinnamic acid and
methanol.
Deserpedine is the demethoxylated derivative of reserpine. It lacks the
methoxyl group on ring "A". On hydrolysis it yields deserpic acid,
trimethoxybenzoic and methanol.
Estimation of reserpine
Reserpine is a weakly basic alkaloid that could not be determined by the
usual titrimetric methods. Several other techniques have been deviced for its
estimation including:
Non-aqueous titration. .1
Fluorimetric estimation. .2
Spectrophotometric determination. .3
.4
Biological assay.
Tests for identification
Vanillin /HCl reagent (1%): gives a violet color with reserpine. .1
90