Page 46 - Cell biology PDG 2024
P. 46
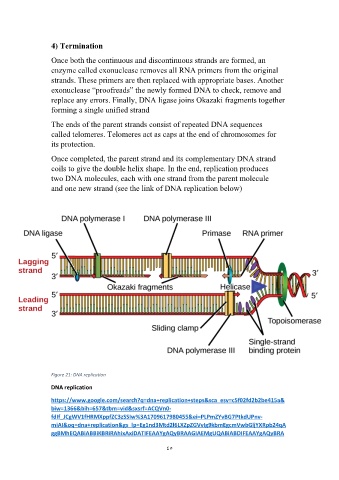
4) Termination
Once both the continuous and discontinuous strands are formed, an
enzyme called exonuclease removes all RNA primers from the original
strands. These primers are then replaced with appropriate bases. Another
exonuclease “proofreads” the newly formed DNA to check, remove and
replace any errors. Finally, DNA ligase joins Okazaki fragments together
forming a single unified strand
The ends of the parent strands consist of repeated DNA sequences
called telomeres. Telomeres act as caps at the end of chromosomes for
its protection.
Once completed, the parent strand and its complementary DNA strand
coils to give the double helix shape. In the end, replication produces
two DNA molecules, each with one strand from the parent molecule
and one new strand (see the link of DNA replication below)
Figure 21: DNA replication
DNA replication
https://www.google.com/search?q=dna+replication+steps&sca_esv=c5f02fd2b2be415a&
biw=1366&bih=657&tbm=vid&sxsrf=ACQVn0-
fdIf_JCgWV1fHRMXppfZC3zSSIw%3A1709617980455&ei=PLPmZYvBG7PtkdUPnv-
miAI&oq=dna+replication&gs_lp=Eg1nd3Mtd2l6LXZpZGVvIg9kbmEgcmVwbGljYXRpb24qA
ggBMhEQABiABBiKBRiRAhixAxiDATIFEAAYgAQyBRAAGIAEMgUQABiABDIFEAAYgAQyBRA
٤٥