Page 8 - Cell biology PDG 2024
P. 8
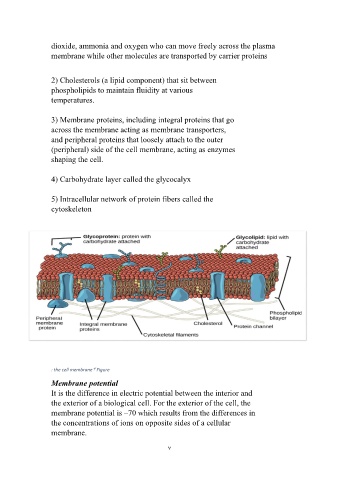
dioxide, ammonia and oxygen who can move freely across the plasma
membrane while other molecules are transported by carrier proteins
2) Cholesterols (a lipid component) that sit between
phospholipids to maintain fluidity at various
temperatures.
3) Membrane proteins, including integral proteins that go
across the membrane acting as membrane transporters,
and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer
(peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes
shaping the cell.
4) Carbohydrate layer called the glycocalyx
5) Intracellular network of protein fibers called the
cytoskeleton
: the cell membrane۳ Figure
Membrane potential
It is the difference in electric potential between the interior and
the exterior of a biological cell. For the exterior of the cell, the
membrane potential is –70 which results from the differences in
the concentrations of ions on opposite sides of a cellular
membrane.
۷