Page 37 - Clinical biochemistry
P. 37
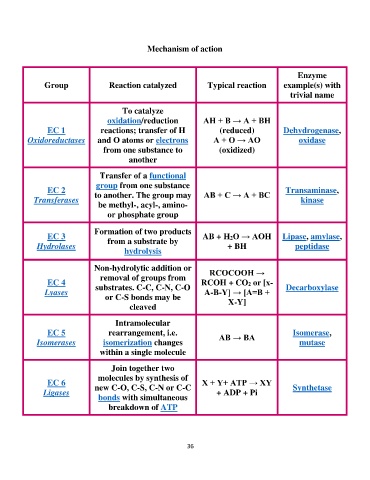
Mechanism of action
Group Reaction catalyzed Typical reaction Enzyme
example(s) with
trivial name
EC 1 To catalyze AH + B → A + BH Dehydrogenase,
Oxidoreductases oxidation/reduction oxidase
reactions; transfer of H (reduced)
and O atoms or electrons A + O → AO
from one substance to
(oxidized)
another
EC 2 Transfer of a functional AB + C → A + BC Transaminase,
Transferases group from one substance kinase
to another. The group may
be methyl-, acyl-, amino-
or phosphate group
EC 3 Formation of two products AB + H2O → AOH Lipase, amylase,
Hydrolases from a substrate by + BH peptidase
hydrolysis
EC 4 Non-hydrolytic addition or RCOCOOH → Decarboxylase
Lyases removal of groups from
RCOH + CO2 or [x-
substrates. C-C, C-N, C-O A-B-Y] → [A=B +
or C-S bonds may be
cleaved X-Y]
EC 5 Intramolecular AB → BA Isomerase,
Isomerases rearrangement, i.e. mutase
isomerization changes
within a single molecule
EC 6 Join together two X + Y+ ATP → XY Synthetase
Ligases molecules by synthesis of + ADP + Pi
new C-O, C-S, C-N or C-C
bonds with simultaneous
breakdown of ATP
36