Page 104 - Pharm.Org.Chem-I 02-06-05-101
P. 104
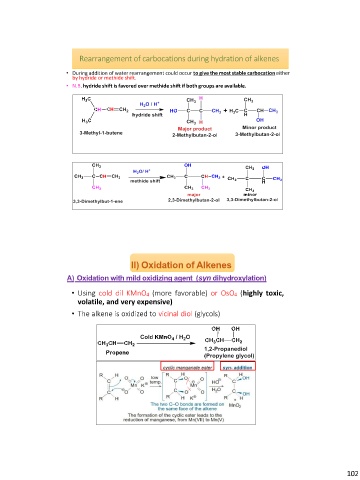
Rearrangement of carbocations during hydration of alkenes
• During addition of water rearrangement could occur to give the most stable carbocation either
by hydride or methide shift.
• N.B. hydride shift is favored over methide shift if both groups are available.
II) Oxidation of Alkenes
A) Oxidation with mild oxidizing agent (syn dihydroxylation)
• Using cold dil KMnO4 (more favorable) or OsO4 (highly toxic,
volatile, and very expensive)
• The alkene is oxidized to vicinal diol (glycols)
102