Page 91 - Pharm.Org.Chem-I 02-06-05-101
P. 91
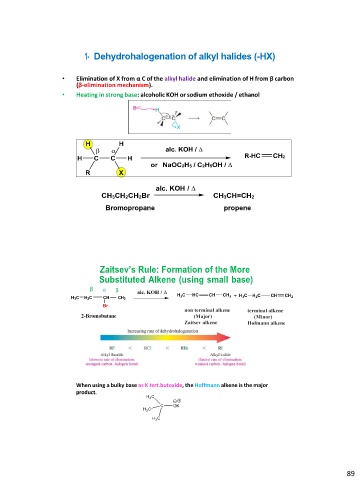
1- Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides (-HX)
• Elimination of X from α C of the alkyl halide and elimination of H from β carbon
(β-elimination mechanism).
• Heating in strong base: alcoholic KOH or sodium ethoxide / ethanol
R-
alc. KOH / CH3CH=CH2
CH3CH2CH2Br propene
Bromopropane
Zaitsev’s Rule: Formation of the More
Substituted Alkene (using small base)
β αβ alc. KOH /
H3C H2C CH CH3
Br
2-Bromobutane
When using a bulky base as K tert.butoxide, the Hoffmann alkene is the major
product.
89