Page 3 - Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry II - Pharm D Clinical- 07-PA202
P. 3
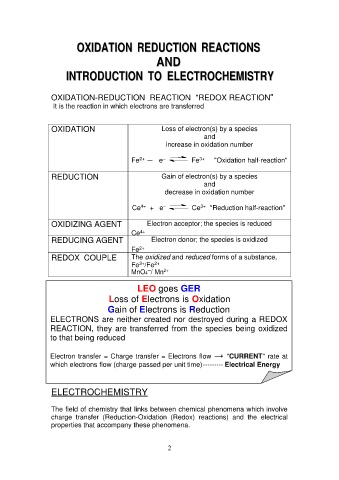
OXIDATION REDUCTION REACTIONS
AND
INTRODUCTION TO ELECTROCHEMISTRY
OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION "REDOX REACTION"
It is the reaction in which electrons are transferred
OXIDATION Loss of electron(s) by a species
and
increase in oxidation number
Fe2+ ─ e– Fe3+ "Oxidation half-reaction"
REDUCTION Gain of electron(s) by a species
and
decrease in oxidation number
Ce4+ + e– Ce3+ "Reduction half-reaction"
OXIDIZING AGENT Electron acceptor; the species is reduced
REDUCING AGENT
REDOX COUPLE Ce4+
Electron donor; the species is oxidized
Fe2+
The oxidized and reduced forms of a substance,
Fe3+/Fe2+
MnO4─/ Mn2+
LEO goes GER
Loss of Electrons is Oxidation
Gain of Electrons is Reduction
ELECTRONS are neither created nor destroyed during a REDOX
REACTION, they are transferred from the species being oxidized
to that being reduced
Electron transfer = Charge transfer = Electrons flow → "CURRENT" rate at
which electrons flow (charge passed per unit time)--------- Electrical Energy
ELECTROCHEMISTRY
The field of chemistry that links between chemical phenomena which involve
charge transfer (Reduction-Oxidation (Redox) reactions) and the electrical
properties that accompany these phenomena.
2