Page 28 - Statistics presented by Dr. Sara Ismail Aborass
P. 28
9/8/2023
1. Random Errors
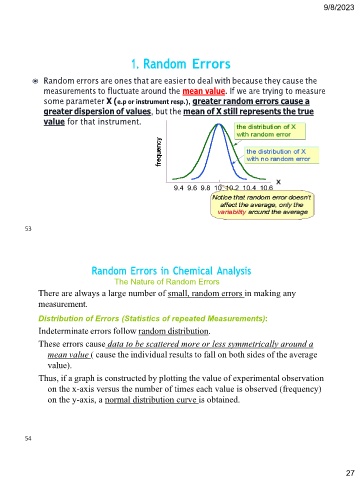
◉ Random errors are ones that are easier to deal with because they cause the
measurements to fluctuate around the mean value. If we are trying to measure
some parameter X (e.p or instrument resp.), greater random errors cause a
greater dispersion of values, but the mean of X still represents the true
value for that instrument.
53
Random Errors in Chemical Analysis
The Nature of Random Errors
There are always a large number of small, random errors in making any
measurement.
Distribution of Errors (Statistics of repeated Measurements):
Indeterminate errors follow random distribution.
These errors cause data to be scattered more or less symmetrically around a
mean value ( cause the individual results to fall on both sides of the average
value).
Thus, if a graph is constructed by plotting the value of experimental observation
on the x-axis versus the number of times each value is observed (frequency)
on the y-axis, a normal distribution curve is obtained.
54
27