Page 87 - MNU-PM503 Parasitology practical book
P. 87
Pharm D- Clinical Pharmacy Program Third Level Parasitology and virology (PM503)
Viral infection
This laboratory section will define and discuss the basic principles of viral
infection, the entire process by which viruses cause disease. Viral disease is a sum
of the effects on the host of virus replication and of the immune response.
Viral Entry
• Three requirements must be satisfied to ensure successful infection in an individual
host:
• Sufficient virus must be available to initiate infection
• Cells at the site of infection must be accessible, susceptible, and
permissive for the virus
• Local host anti-viral defense systems must be absent or initially ineffective.
- To infect its host, a virus must first enter cells at a body surface.
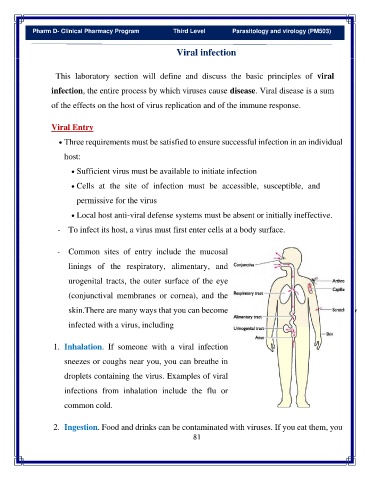
- Common sites of entry include the mucosal
linings of the respiratory, alimentary, and
urogenital tracts, the outer surface of the eye
(conjunctival membranes or cornea), and the
skin.There are many ways that you can become
infected with a virus, including
1. Inhalation. If someone with a viral infection
sneezes or coughs near you, you can breathe in
droplets containing the virus. Examples of viral
infections from inhalation include the flu or
common cold.
2. Ingestion. Food and drinks can be contaminated with viruses. If you eat them, you
81