Page 15 - Semester-IV-Electronics
P. 15
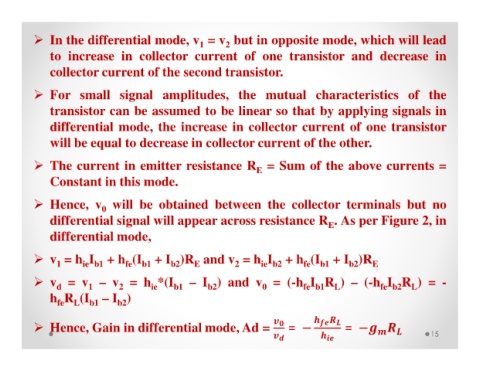
In the differential mode, v = v but in opposite mode, which will lead
1
2
to increase in collector current of one transistor and decrease in
collector current of the second transistor.
For small signal amplitudes, the mutual characteristics of the
transistor can be assumed to be linear so that by applying signals in
differential mode, the increase in collector current of one transistor
will be equal to decrease in collector current of the other.
The current in emitter resistance R = Sum of the above currents =
E
Constant in this mode.
Hence, v will be obtained between the collector terminals but no
0
differential signal will appear across resistance R . As per Figure 2, in
E
differential mode,
v = h I + h (I + I )R and v = h I + h (I + I )R E
ie b2
b1
fe
b1
fe
2
b2
E
b2
ie b1
1
v = v – v = h *(I b1 – I ) and v = (-h I R ) – (-h I R ) = -
d
fe b1
L
0
ie
L
2
1
fe b2
b2
h R (I – I )
b1
L
fe
b2
Hence, Gain in differential mode, Ad = = − = −
15