Page 12 - 53-Peptic ulcer diseases (Loét dạ dày)
P. 12
816 PART VI Stomach and Duodenum
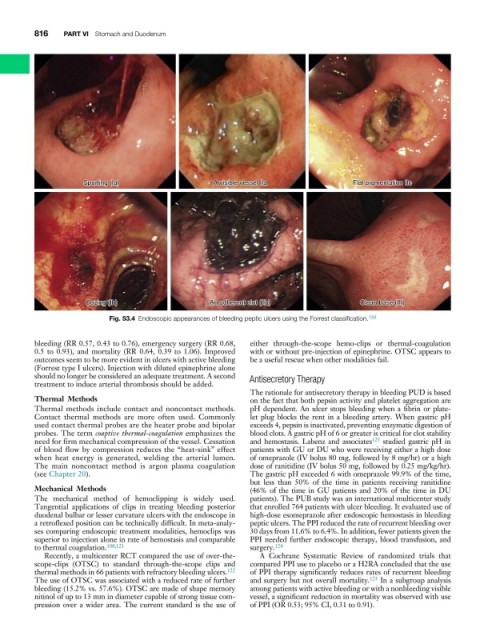
Spurting (Ia) A visible vessel IIa Flat pigmentation IIc
Oozing (Ib) An adherent clot (IIb) Clean base (III)
Fig. 53.4 Endoscopic appearances of bleeding peptic ulcers using the Forrest classification. 139
bleeding (RR 0.57, 0.43 to 0.76), emergency surgery (RR 0.68, either through-the-scope hemo-clips or thermal-coagulation
0.5 to 0.93), and mortality (RR 0.64, 0.39 to 1.06). Improved with or without pre-injection of epinephrine. OTSC appears to
outcomes seem to be more evident in ulcers with active bleeding be a useful rescue when other modalities fail.
(Forrest type I ulcers). Injection with diluted epinephrine alone
should no longer be considered an adequate treatment. A second Antisecretory Therapy
treatment to induce arterial thrombosis should be added.
The rationale for antisecretory therapy in bleeding PUD is based
Thermal Methods on the fact that both pepsin activity and platelet aggregation are
Thermal methods include contact and noncontact methods. pH dependent. An ulcer stops bleeding when a fibrin or plate-
Contact thermal methods are more often used. Commonly let plug blocks the rent in a bleeding artery. When gastric pH
used contact thermal probes are the heater probe and bipolar exceeds 4, pepsin is inactivated, preventing enzymatic digestion of
probes. The term coaptive thermal-coagulation emphasizes the blood clots. A gastric pH of 6 or greater is critical for clot stability
need for firm mechanical compression of the vessel. Cessation and hemostasis. Labenz and associates 123 studied gastric pH in
of blood flow by compression reduces the “heat-sink” effect patients with GU or DU who were receiving either a high dose
when heat energy is generated, welding the arterial lumen. of omeprazole (IV bolus 80 mg, followed by 8 mg/hr) or a high
The main noncontact method is argon plasma coagulation dose of ranitidine (IV bolus 50 mg, followed by 0.25 mg/kg/hr).
(see Chapter 20). The gastric pH exceeded 6 with omeprazole 99.9% of the time,
but less than 50% of the time in patients receiving ranitidine
Mechanical Methods (46% of the time in GU patients and 20% of the time in DU
The mechanical method of hemoclipping is widely used. patients). The PUB study was an international multicenter study
Tangential applications of clips in treating bleeding posterior that enrolled 764 patients with ulcer bleeding. It evaluated use of
duodenal bulbar or lesser curvature ulcers with the endoscope in high-dose esomeprazole after endoscopic hemostasis in bleeding
a retroflexed position can be technically difficult. In meta-analy- peptic ulcers. The PPI reduced the rate of recurrent bleeding over
ses comparing endoscopic treatment modalities, hemoclips was 30 days from 11.6% to 6.4%. In addition, fewer patients given the
superior to injection alone in rate of hemostasis and comparable PPI needed further endoscopic therapy, blood transfusion, and
to thermal coagulation. 108,121 surgery. 124
Recently, a multicenter RCT compared the use of over-the- A Cochrane Systematic Review of randomized trials that
scope-clips (OTSC) to standard through-the-scope clips and compared PPI use to placebo or a H2RA concluded that the use
thermal methods in 66 patients with refractory bleeding ulcers. 122 of PPI therapy significantly reduces rates of recurrent bleeding
The use of OTSC was associated with a reduced rate of further and surgery but not overall mortality. 125 In a subgroup analysis
bleeding (15.2% vs. 57.6%). OTSC are made of shape memory among patients with active bleeding or with a nonbleeding visible
nitinol of up to 13 mm in diameter capable of strong tissue com- vessel, a significant reduction in mortality was observed with use
pression over a wider area. The current standard is the use of of PPI (OR 0.53; 95% CI, 0.31 to 0.91).