Page 166 - NUMINO TG_5A
P. 166
10Multiply Mixed Numbers Unit
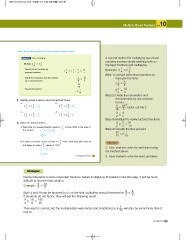
Students should multiply after writing the mixed numbers as improper fractions.
Method 2 Use renaming. A second method for multiplying two mixed
2 1 3 3 numbers involves simply rewriting both as
4 5
Multiply improper fractions and multiplying.
Rewrite mixed numbers as 2 1 3 3 = 9 18 Example: 2 1 3 3
improper fractions. 4 5 4 5 4 5
9 Step 1: Convert both mixed numbers to
Divide the numerator and denominator =9 18 improper fractions.
by a common factor. 4 5
1 9
2 2 4 4
= 81
10
3 18
Rewrite the fraction. 1 3 5 5
10
= 8
Step 2: Divide the numerators and
2 . Multiply mixed numbers using the method above. denominators by any common
a. 1 1 b. 2 2 factors. 9
3 4 3 5
2 1 = 2 11 4 2 = 11 1 9 18 , factor out the 2.
12 5 42 5
c. 1 3 1 d. 4 1 99
2 4 8 7 5
3 1 =6 3 4 = 15 25
Step 3: Multiply the newly-factored fractions.
3 . Solve the word problems. 9 9 81
a. Each side of a square-shaped carpet is 1 2 m long. What is the area of 2 5 10
this carpet? 5
1 2 1 2 =1 24 Step 4: Simplify the final product.
5 5 25
81 1
1 24 m2 10 8 10
25
b. A baker can make 1 p25iecp1eie31coe=f sc3 ao51kfecainke1?13 hours. How long will it take for
this baker to make 2 2. Have students solve the problems using
the method above.
22
5 3. Have students solve the word problems
3 1 hours
5
10. Multiply Mixed Numbers 93
Remind students to factor improper fractions before multiplying. If students miss this step, it will be more
difficult to find the final solution.
Example: 9 18
4 5
Both 4 and 18 can be factored by 2, so the final multipliers should therefore be 9 9 .
2 5
If students do not factor, they will get the following result.
9 18 162
4 5 20
This result is correct, but the multiplication was harder and simplifying to 8 1 will also be more tricky than it
10
has to.
5A Unit 10 149
Students should multiply after writing the mixed numbers as improper fractions.
Method 2 Use renaming. A second method for multiplying two mixed
2 1 3 3 numbers involves simply rewriting both as
4 5
Multiply improper fractions and multiplying.
Rewrite mixed numbers as 2 1 3 3 = 9 18 Example: 2 1 3 3
improper fractions. 4 5 4 5 4 5
9 Step 1: Convert both mixed numbers to
Divide the numerator and denominator =9 18 improper fractions.
by a common factor. 4 5
1 9
2 2 4 4
= 81
10
3 18
Rewrite the fraction. 1 3 5 5
10
= 8
Step 2: Divide the numerators and
2 . Multiply mixed numbers using the method above. denominators by any common
a. 1 1 b. 2 2 factors. 9
3 4 3 5
2 1 = 2 11 4 2 = 11 1 9 18 , factor out the 2.
12 5 42 5
c. 1 3 1 d. 4 1 99
2 4 8 7 5
3 1 =6 3 4 = 15 25
Step 3: Multiply the newly-factored fractions.
3 . Solve the word problems. 9 9 81
a. Each side of a square-shaped carpet is 1 2 m long. What is the area of 2 5 10
this carpet? 5
1 2 1 2 =1 24 Step 4: Simplify the final product.
5 5 25
81 1
1 24 m2 10 8 10
25
b. A baker can make 1 p25iecp1eie31coe=f sc3 ao51kfecainke1?13 hours. How long will it take for
this baker to make 2 2. Have students solve the problems using
the method above.
22
5 3. Have students solve the word problems
3 1 hours
5
10. Multiply Mixed Numbers 93
Remind students to factor improper fractions before multiplying. If students miss this step, it will be more
difficult to find the final solution.
Example: 9 18
4 5
Both 4 and 18 can be factored by 2, so the final multipliers should therefore be 9 9 .
2 5
If students do not factor, they will get the following result.
9 18 162
4 5 20
This result is correct, but the multiplication was harder and simplifying to 8 1 will also be more tricky than it
10
has to.
5A Unit 10 149