Page 111 - The Miracle of Electricity in the Body
P. 111
109
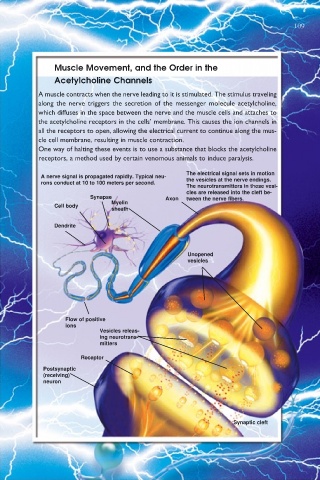
Muscle Movement, and the Order in the
Acetylcholine Channels
A muscle contracts when the nerve leading to it is stimulated. The stimulus traveling
along the nerve triggers the secretion of the messenger molecule acetylcholine,
which diffuses in the space between the nerve and the muscle cells and attaches to
the acetylcholine receptors in the cells’ membrane. This causes the ion channels in
all the receptors to open, allowing the electrical current to continue along the mus-
cle cell membrane, resulting in muscle contraction.
One way of halting these events is to use a substance that blocks the acetylcholine
receptors, a method used by certain venomous animals to induce paralysis.
The electrical signal sets in motion
A nerve signal is propagated rapidly. Typical neu- the vesicles at the nerve endings.
rons conduct at 10 to 100 meters per second.
The neurotransmitters in these vesi-
cles are released into the cleft be-
Synapse Axon tween the nerve fibers.
Myelin
Cell body
sheath
Dendrite
Unopened
vesicles
Flow of positive
ions
Vesicles releas-
ing neurotrans-
mitters
Receptor
Postsynaptic
(receiving)
neuron
Synaptic cleft