Page 477 - Corporate Finance PDF Final new link
P. 477
NPP
BRILLIANT’S Analysis of Risk and Uncertainty in Investment Decisions 477
Limitations of Decision Tree Approach {S>[gOZ Q´>r EàmoM H$s gr_mE±
1. Decision tree approach requires large 1. {S>[gOZ Q´>r EàmoM Ho$ \$m°å`y©boeZ hoVw ~‹S>r _mÌm _|
volume of data for its formulation.
S>mQ>m H$s Amdí`H$Vm hmoVr h¡Ÿ&
2. This approach becomes more and more 2. O¡go-O¡go ñQ>oOog ~‹T>Vr h¡, `h EàmoM O{Q>b
complicated as the number of stages hmoVr h¡Ÿ&
increase.
Illustration 5.2.1
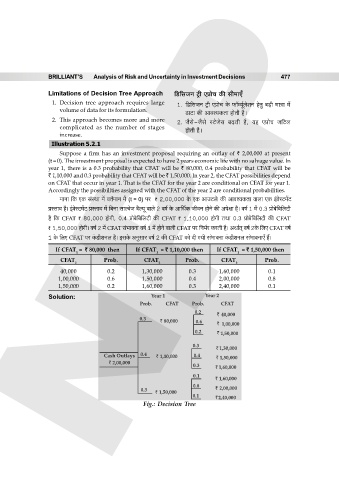
Suppose a firm has an investment proposal requiring an outlay of ` 2,00,000 at present
(t = 0). The investment proposal is expected to have 2 years economic life with no salvage value. In
year 1, there is a 0.3 probability that CFAT will be ` 80,000, 0.4 probability that CFAT will be
` 1,10,000 and 0.3 probability that CFAT will be ` 1,50,000. In year 2, the CFAT possibilities depend
on CFAT that occur in year 1. That is the CFAT for the year 2 are conditional on CFAT for year 1.
Accordingly the possibilities assigned with the CFAT of the year 2 are conditional probabilities.
_mZm {H$ EH$ g§ñWm _| dV©_mZ _| (t = 0) na ` 2,00,000 Ho$ EH$ AmCQ>bo> H$s Amdí`H$Vm dmbm EH$ B§doñQ>_|Q
àñVmd h¡& B§doñQ>‘|Q> àñVmd ‘| {~Zm gmëdoO d¡ë¶y dmbo 2 df© Ho$ Am{W©H$ OrdZ hmoZo H$s Anojm h¡& df© 1 ‘| 0.3 àmo~o{~{bQ>r
h¡ {H$ CFAT ` 80,000 hmoJr, 0.4 àmo~o{~{bQ>r H$s CFAT ` 1,10,000 hmoJr VWm 0.3 àmo~o{~{bQ>r H$s CFAT
` 1,50,000 hmoJr& df© 2 ‘| CFAT g§^mdZm df© 1 ‘| hmoZo dmbr CFAT na {Z^©a H$aVr h¡& AWm©V² df© 2Ho$ {bE CFAT df©
1 Ho$ {bE CFAT na H§$S>reZb h¡& BgHo$ AZwgma df© 2 H$s CFAT H$mo Xr J¶r g§^mdZm H§$S>reZb g§^mdZmE± h¢&
If CFAT = ` 80,000 then If CFAT = ` 1,10,000 then If CFAT = ` 1,50,000 then
1 1 1
CFAT Prob. CFAT Prob. CFAT Prob.
2 2 2
40,000 0.2 1,30,000 0.3 1,60,000 0.1
1,00,000 0.6 1,50,000 0.4 2,00,000 0.8
1,50,000 0.2 1,60,000 0.3 2,40,000 0.1
Solution: Year 1 Year 2
Prob. CFAT Prob. CFAT
0.2
` 40,000
0.3
` 80,000 0.6 ` 1,00,000
0.2 ` 1,50,000
0.3
` 1,30,000
Cash Outlays 0.4 ` 1,10,000 0.4 ` 1,50,000
` 2,00,000
0.3 ` 1,60,000
0.1
` 1,60,000
0.8
0.3 ` 2,00,000
` 1,50,000
0.1 ` 2,40,000
Fig.: Decision Tree