Page 76 - NEW Armstrong Book - 2
P. 76
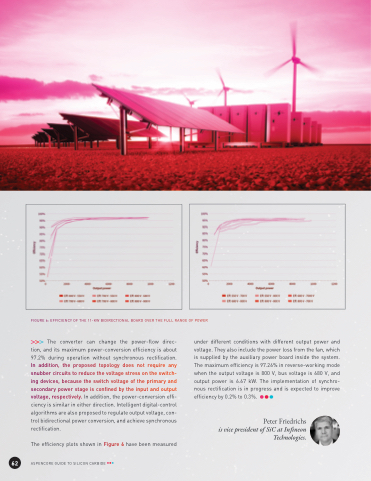
FIGURE 6: EFFICIENCY OF THE 11-KW BIDIRECTIONAL BOARD OVER THE FULL RANGE OF POWER
The converter can change the power-flow direc- tion, and its maximum power-conversion efficiency is about 97.2% during operation without synchronous rectification. In addition, the proposed topology does not require any snubber circuits to reduce the voltage stress on the switch- ing devices, because the switch voltage of the primary and secondary power stage is confined by the input and output voltage, respectively. In addition, the power-conversion effi- ciency is similar in either direction. Intelligent digital-control algorithms are also proposed to regulate output voltage, con- trol bidirectional power conversion, and achieve synchronous rectification.
The efficiency plots shown in Figure 6 have been measured ASPENCORE GUIDE TO SILICON CARBIDE
under different conditions with different output power and voltage. They also include the power loss from the fan, which is supplied by the auxiliary power board inside the system. The maximum efficiency is 97.26% in reverse-working mode when the output voltage is 800 V, bus voltage is 680 V, and output power is 6.67 kW. The implementation of synchro- nous rectification is in progress and is expected to improve efficiency by 0.2% to 0.3%.
Peter Friedrichs
is vice president of SiC at Infineon Technologies.
62