Page 12 - model 1
P. 12
the nerve fibre and the membrane of the muscle fibre change its permeability so, the
sodium ions pass through the membrane causing depolarization (+ve inside and -ve
outside) this leads to muscle contraction.
5. After a part of a second the potential difference of the muscle fibre membrane returns
to its normal state “repolarization” due to the action of Cholinesterase enzyme, found
in large amount at neuromuscular junctions which destroys acetylcholine into choline
and cetic acid, so its acion. The membrane permeability to ions returns to the resting
state it is now ready to be stimulated and respond again and so on.
Mechanism of Muscle contraction (The theory of sliding filaments)
The most acceptable theory for muscle contraction is the theory of Huxely. This
theory depends on the microscopic sturcture of the muscle fibre which consists of
myofibrils. Each myofibrils consists of thin actin filaments and thick myosin filaments
as previously mentioned. After comparing a muscle fibre in a state of contraction with
another fibre in a state of relaxation using electorn microscope.
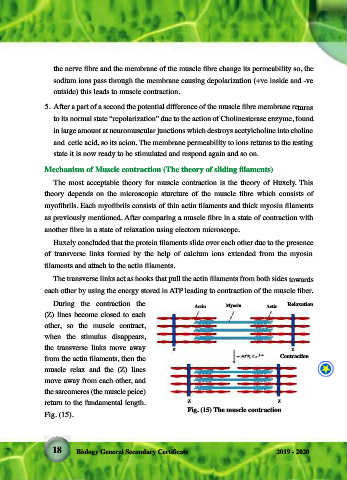
Huxely concluded that the protein filaments slide over each other due to the presence
ATP تايئزج ىف ةنزخمل� ةقاطل� ةدعاس�مب بحس�ت فيطاطخك ةس�رعتس�مل� طب�ورل� هذه لمعت امدنع
of transverse links formed by the help of calcium ions extended from the myosin
.ةيلس�عل� ةفيلل� ض�ابقن� هنع جتنيف ض�عبل� اهس�عب هاجتاب نيتكلا� طويخ نم ةرواجتمل� تاعومجمل�
filaments and attach to the actin filaments.
ط�ورل� دعتبت هبنمل� ل�وز دنعو ،ةلس�عل� ض�بقنت �ذكهو ،اهس�عب نم )Z( طوطخ براقتت اس�بقنلا� ءانثأ�
ةيلس�عل� عطقل� دوعتو هس�عب نع )Z( طوطخ دعابتيو ةلس�عل� طس�بنتف نيتكألا� طويخ نع ةس�رعتس�مل�
The transverse links act as hooks that pull the actin filaments from both sides towards
.)15( لكس� ىس�اس�ألا� اهلوط ىلإ�
each other by using the energy stored in ATP leading to contraction of the muscle fiber.
During the contraction the Actin Myosin Actin Relaxation
(Z) lines become closed to each
other, so the muscle contract,
when the stimulus disappears,
the transverse links move away
from the actin filaments, then the Contraction
muscle relax and the (Z) lines
move away from each other, and
the sarcomeres (the muscle peice)
return to the fundamental length. Z Z
ىلش�علا ص�ابقنلا )15( لكش�
Fig. (15) The muscle contraction
Fig. (15).
،نيتكألا� طويخ نع ةس�رعتس�مل� طب�ورل� لس�ف ىف ATP ىف ةنزتخمل� ةقاطل� نم ءزج ةلس�عل� كلهتس�ت
لظتف نيتكألا� طويخ نع ةس�رعتس�مل� طب�ورل� لاس�فن� مدع ىلإ� كلذ ىدؤوي دق ATP ض�قانت دنع �ذل
.طاس�بنلا� ىلع ةرداق ريغو ض�ابقن� ةلاح ىف ةلس�عل�
18 Biology General Secondary Certificate 2019 - 2020 2017 - 2018 Shorouk Press
طويخ نع اهلاس�فن�و ض�ابقنلا� ءانثأ� نيتكألا� طويخب ةس�رعتس�مل� طب�ورل� لاس�ت� ىتيلمع جاتحت
.ATP تائزج ىف ةنزخمل� ةقاطل� ىلإ� طاس�بنلا� نع نيتكألا�
رس�فت نأ� عطتس�ت مل اهنأ� لاإ� )ةططخمل�( ةيلكيهل� تلاس�عل� ض�ابقن� رس�فت ىتل� ةيرظنل� هذه دوجو مغرو
ىف ةينيتوربل� طويخل� نأ� ىلإ� ريس�ت ىتل� ةيملعل� ريراقتل� ض�عب دوجو مغر ءاس�لمل� تلاس�عل� ض�ابقن� ةيلآ�
� تلاس ىف ةينيتكألا� طويخل ريبك دح ىلإ� هب �ي عون نم نوكتت ءاس�لمل� تلاس فايلأ�
Motor Unit : ةيكرحلا ةدحولا
ةيكرحل ةدحول ىلع فرعتن نأ� انه دبلا ىل ض�ابقنلا ةيلمعل ةيكيناكيمل رهاظمل ىلع فرعتن ىكل
عيمج ض�ابقن ةل �حم لاإ� وه ام تلا ض�ابقن نلا ،ةيلكيهل ةل �علل ةيفيظول ةدحول ربتعت ىتل
. �علل ةفلؤومل ةيكرحل� ت�
فس�ويلا زور عباطم