Page 33 - Brochure_Tips_and_Tricks_BAT_BD_Neat
P. 33
Y E A STS CHAR AC TERISTIC S Y E A STS CHAR AC TERISTIC S
Apparent Degree of Fermentation (ADF)
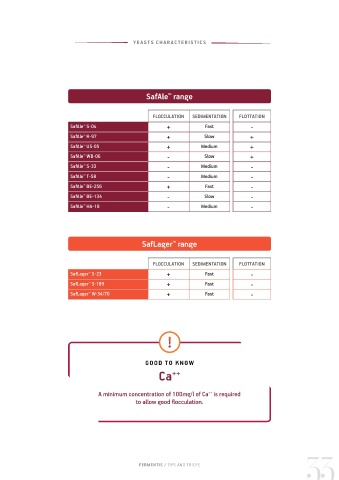
SafAle range
™
THE TABLE BELOW SHOWS THE APPARENT DEGREE OF FERMENTATION (ADF) in % after
fermentation for each strain. FLOCCULATION SEDIMENTATION FLOTTATION
SafAle S-04 + Fast -
™
SafAle K-97 + Slow +
™
SafAle range
™
SafAle US-05 + Medium +
™
SafAle WB-06 - Slow +
™
ADF
SafAle S-33 - Medium -
™
SafAle S-04 74-82%
™
SafAle T-58 - Medium -
™
SafAle K-97 80-84%
™
SafAle BE-256 + Fast -
™
SafAle US-05 78-82%
™
™
SafAle BE-134 - Slow -
™
SafAle WB-06 86-90%
SafAle HA-18 - Medium -
™
SafAle S-33 68-72%
™
SafAle T-58 72-78%
™
SafAle BE-256 82-86%
™
™
SafAle BE-134 89-93% SafLager range
™
SafAle HA-18 98-102%
™
FLOCCULATION SEDIMENTATION FLOTTATION
SafLager S-23 + Fast -
™
SafLager range SafLager S-189 + Fast -
™
™
™
SafLager W-34/70 + Fast -
ADF
SafLager S-23 80-84%
™
SafLager S-189 80-84%
™
SafLager W-34/70 80-84%
™
Flocculation GOOD TO KNOW
Ca ++
FLOCCULATION IS THE ABILITY OF YEAST CELLS TO FORM AGGREGATES. It is the ability
of yeast to raise in the foam at the end of fermentation. If the yeast is not A minimum concentration of 100mg/l of Ca is required
++
remaining in the foam at the end of fermentation, a highly flocculent yeast to allow good flocculation.
will sediment fast and create a clear beer with little cells in suspension. On the
contrary, a low flocculent yeast will sediment slowly and leave the beer hazy
for a longer period of time.
32 FERMENTIS / TIPS AND TRICKS FERMENTIS / TIPS AND TRICKS 33