Page 31 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 31
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
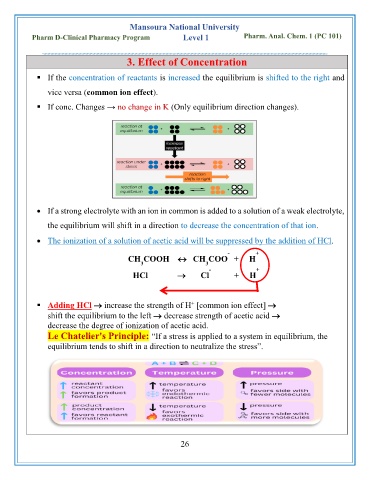
3. Effect of Concentration
▪ If the concentration of reactants is increased the equilibrium is shifted to the right and
vice versa (common ion effect).
▪ If conc. Changes → no change in K (Only equilibrium direction changes).
• If a strong electrolyte with an ion in common is added to a solution of a weak electrolyte,
the equilibrium will shift in a direction to decrease the concentration of that ion.
• The ionization of a solution of acetic acid will be suppressed by the addition of HCl.
- +
CH COOH CH COO + H
3 3
- +
HCl → Cl + H
+
▪ Adding HCl → increase the strength of H [common ion effect] →
shift the equilibrium to the left → decrease strength of acetic acid →
decrease the degree of ionization of acetic acid.
Le Chatelier's Principle: “If a stress is applied to a system in equilibrium, the
equilibrium tends to shift in a direction to neutralize the stress”.
26