Page 10 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 10
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
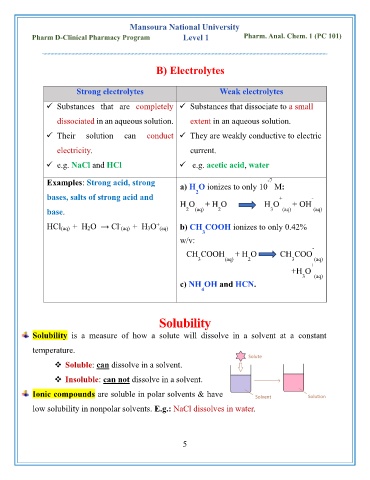
B) Electrolytes
Strong electrolytes Weak electrolytes
✓ Substances that are completely ✓ Substances that dissociate to a small
dissociated in an aqueous solution. extent in an aqueous solution.
✓ Their solution can conduct ✓ They are weakly conductive to electric
electricity. current.
✓ e.g. NaCl and HCl ✓ e.g. acetic acid, water
Examples: Strong acid, strong -7
a) H O ionizes to only 10 M:
bases, salts of strong acid and 2 + -
H O + H O H O + OH
base. 2 (aq) 2 3 (aq) (aq)
-
+
HCl (aq) + H 2O → Cl (aq) + H 3O (aq) b) CH COOH ionizes to only 0.42%
3
w/v:
-
CH COOH + H O CH COO
3 (aq) 2 3 (aq)
+
+H O
3 (aq)
c) NH OH and HCN.
4
Solubility
Solubility is a measure of how a solute will dissolve in a solvent at a constant
temperature.
❖ Soluble: can dissolve in a solvent.
❖ Insoluble: can not dissolve in a solvent.
Ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents & have
low solubility in nonpolar solvents. E.g.: NaCl dissolves in water.
5