Page 63 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 63
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
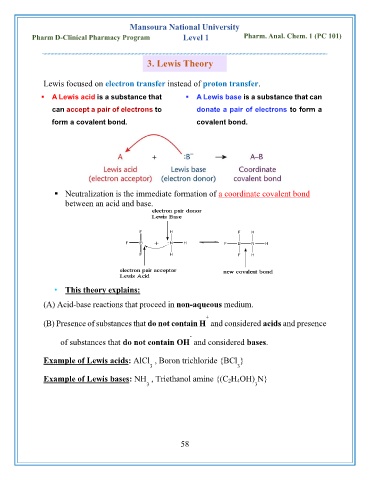
3. Lewis Theory
Lewis focused on electron transfer instead of proton transfer.
▪ A Lewis acid is a substance that ▪ A Lewis base is a substance that can
can accept a pair of electrons to donate a pair of electrons to form a
form a covalent bond. covalent bond.
▪ Neutralization is the immediate formation of a coordinate covalent bond
between an acid and base.
• This theory explains:
(A) Acid-base reactions that proceed in non-aqueous medium.
+
(B) Presence of substances that do not contain H and considered acids and presence
-
of substances that do not contain OH and considered bases.
Example of Lewis acids: AlCl , Boron trichloride {BCl }
3 3
Example of Lewis bases: NH , Triethanol amine {(C 2H 4OH) N}
3 3
58