Page 344 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 344
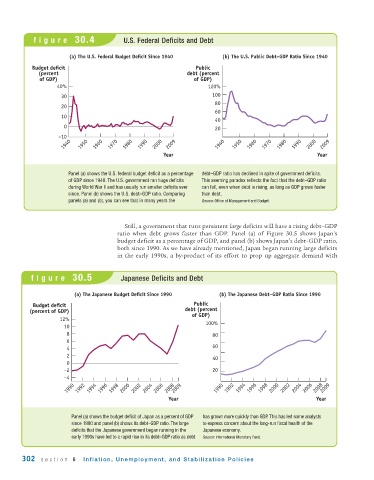
figure 30.4 U.S. Federal Deficits and Debt
(a) The U.S. Federal Budget Deficit Since 1940 (b) The U.S. Public Debt–GDP Ratio Since 1940
Budget deficit Public
(percent debt (percent
of GDP) of GDP)
40% 120%
30 100
80
20
60
10
40
0 20
–10
1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2009 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2009
Year Year
Panel (a) shows the U.S. federal budget deficit as a percentage debt–GDP ratio has declined in spite of government deficits.
of GDP since 1940. The U.S. government ran huge deficits This seeming paradox reflects the fact that the debt–GDP ratio
during World War II and has usually run smaller deficits ever can fall, even when debt is rising, as long as GDP grows faster
since. Panel (b) shows the U.S. debt–GDP ratio. Comparing than debt.
panels (a) and (b), you can see that in many years the Source: Office of Management and Budget.
Still, a government that runs persistent large deficits will have a rising debt–GDP
ratio when debt grows faster than GDP. Panel (a) of Figure 30.5 shows Japan’s
budget deficit as a percentage of GDP, and panel (b) shows Japan’s debt–GDP ratio,
both since 1990. As we have already mentioned, Japan began running large deficits
in the early 1990s, a by -product of its effort to prop up aggregate demand with
figure 30.5 Japanese Deficits and Debt
(a) The Japanese Budget Deficit Since 1990 (b) The Japanese Debt–GDP Ratio Since 1990
Budget deficit Public
(percent of GDP) debt (percent
of GDP)
12%
10 100%
8 80
6
4 60
2 40
0
–2 20
–4
1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2009 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2009
Year Year
Panel (a) shows the budget deficit of Japan as a percent of GDP has grown more quickly than GDP. This has led some analysts
since 1990 and panel (b) shows its debt–GDP ratio. The large to express concern about the long -run fiscal health of the
deficits that the Japanese government began running in the Japanese economy.
early 1990s have led to a rapid rise in its debt–GDP ratio as debt Source: International Monetary Fund.
302 section 6 Inflation, Unemployment, and Stabilization Policies