Page 503 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 503
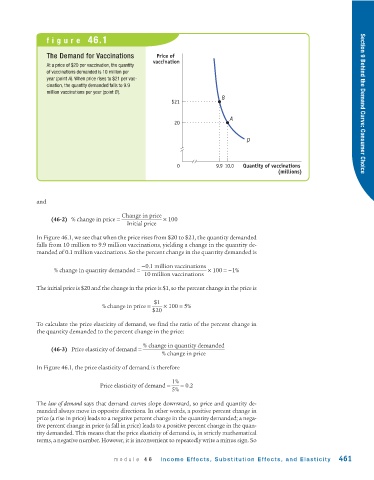
figure 46.1
The Demand for Vaccinations Price of
vaccination
At a price of $20 per vaccination, the quantity
of vaccinations demanded is 10 million per
year (point A). When price rises to $21 per vac-
cination, the quantity demanded falls to 9.9
million vaccinations per year (point B).
B
$21 Section 9 Behind the Demand Curve: Consumer Choice
A
20
D
0 9.9 10.0 Quantity of vaccinations
(millions)
and
(46-2) % change in price = Change in price × 100
Initial price
In Figure 46.1, we see that when the price rises from $20 to $21, the quantity demanded
falls from 10 million to 9.9 million vaccinations, yielding a change in the quantity de-
manded of 0.1 million vaccinations. So the percent change in the quantity demanded is
% change in quantity demanded = −0.1 million vaccinations × 100 = −1%
10 million vaccinations
The initial price is $20 and the change in the price is $1, so the percent change in the price is
$1
% change in price = × 100 = 5%
$20
To calculate the price elasticity of demand, we find the ratio of the percent change in
the quantity demanded to the percent change in the price:
(46-3) Price elasticity of demand = % change in quantity demanded
% change in price
In Figure 46.1, the price elasticity of demand is therefore
Price elasticity of demand = 1% = 0.2
5%
The law of demand says that demand curves slope downward, so price and quantity de-
manded always move in opposite directions. In other words, a positive percent change in
price (a rise in price) leads to a negative percent change in the quantity demanded; a nega-
tive percent change in price (a fall in price) leads to a positive percent change in the quan-
tity demanded. This means that the price elasticity of demand is, in strictly mathematical
terms, a negative number. However, it is inconvenient to repeatedly write a minus sign. So
module 46 Income Effects, Substitution Effects, and Elasticity 461