Page 781 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 781
Private versus Social Costs
Now let’s turn briefly to consider a case in which production of a good
creates external costs—namely, the livestock industry. Whatever it is—
cows, pigs, chicken, sheep, or salmon—livestock farming produces prodi-
gious amounts of what is euphemistically known as “muck.” But that’s
not all: scientists estimate that the amount of methane gas produced by
livestock currently rivals the amount caused by the burning of fossil fuels
in the creation of greenhouse gases. From the point of view of society as a
whole, then, the cost of livestock farming includes both direct production Photodisc
costs (payments for factors of production and inputs) and the external en- Section 14 Market Failure and the Role of Government
vironmental costs imposed as a by-product of farming. The social cost of livestock produc-
When a good like pork involves negative externalities, there is a difference between tion is felt beyond the farm.
the marginal cost to the firm, which we distinguish as the marginal private cost, and
the marginal cost to society, the marginal social cost of a good (or likewise of a service
or activity). The difference between the marginal private cost (MPC) and the marginal
social cost (MSC) is the marginal external cost (MEC)—the increase in external costs to The marginal private cost of a good is
society from an additional unit of the good: the marginal cost of producing that good,
not including any external costs.
(75-2) MSC = MPC + MEC The marginal social cost of a good is
equal to the marginal private cost of
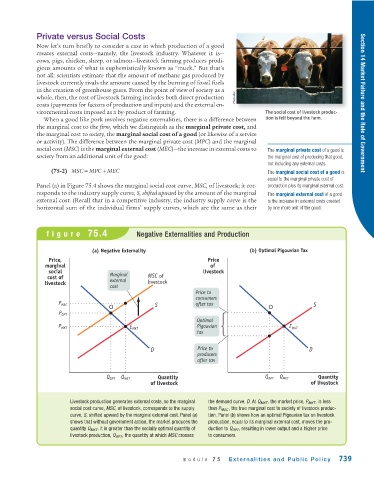
Panel (a) in Figure 75.4 shows the marginal social cost curve, MSC, of livestock; it cor- production plus its marginal external cost.
responds to the industry supply curve, S, shifted upward by the amount of the marginal The marginal external cost of a good
external cost. (Recall that in a competitive industry, the industry supply curve is the is the increase in external costs created
horizontal sum of the individual firms’ supply curves, which are the same as their by one more unit of the good.
figure 75.4 Negative Externalities and Production
(a) Negative Externality (b) Optimal Pigouvian Tax
Price, Price
marginal of
social livestock
cost of Marginal MSC of
external
livestock livestock
cost
Price to
consumers
P MSC after tax S
O S O
P OPT
Optimal
P MKT E MKT Pigouvian E MKT
tax
D Price to D
producers
after tax
Q OPT Q MKT Quantity Q OPT Q MKT Quantity
of livestock of livestock
Livestock production generates external costs, so the marginal the demand curve, D. At Q MKT , the market price, P MKT , is less
social cost curve, MSC, of livestock, corresponds to the supply than P MSC , the true marginal cost to society of livestock produc-
curve, S, shifted upward by the marginal external cost. Panel (a) tion. Panel (b) shows how an optimal Pigouvian tax on livestock
shows that without government action, the market produces the production, equal to its marginal external cost, moves the pro-
quantity Q MKT . It is greater than the socially optimal quantity of duction to Q OPT , resulting in lower output and a higher price
livestock production, Q OPT , the quantity at which MSC crosses to consumers.
module 75 Exter nalities and Public Policy 739